| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
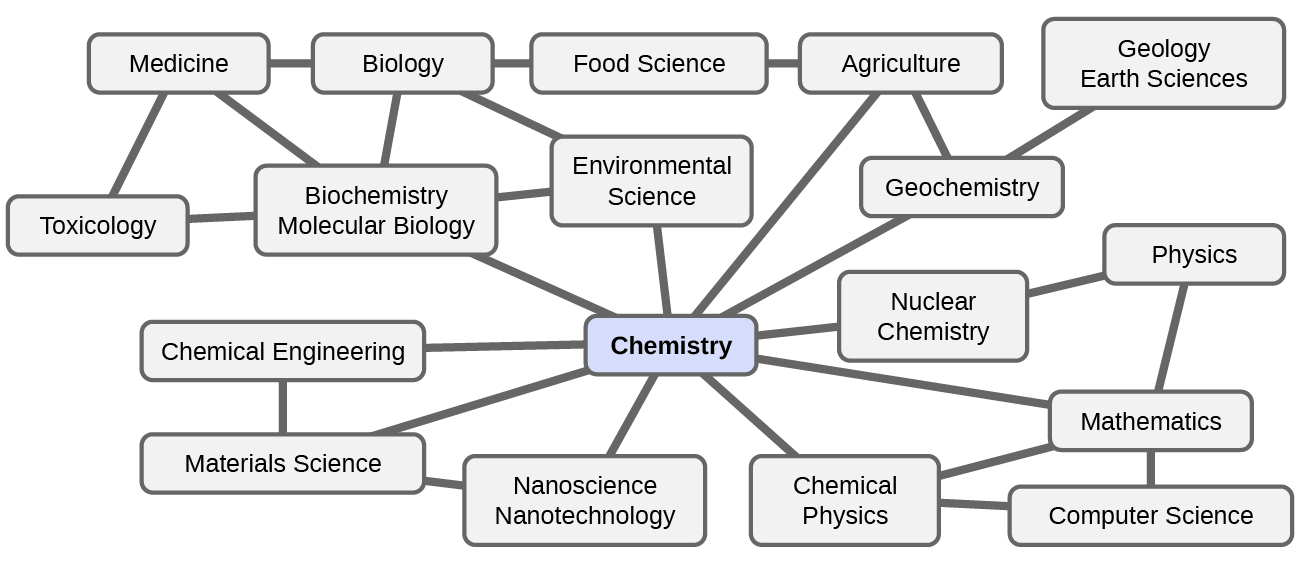
What are some changes in matter that are essential to daily life? Digesting and assimilating food, synthesizing polymers that are used to make clothing, containers, cookware, and credit cards, and refining crude oil into gasoline and other products are just a few examples. As you proceed through this course, you will discover many different examples of changes in the composition and structure of matter, how to classify these changes and how they occurred, their causes, the changes in energy that accompany them, and the principles and laws involved. As you learn about these things, you will be learning chemistry , the study of the composition, properties, and interactions of matter. The practice of chemistry is not limited to chemistry books or laboratories: It happens whenever someone is involved in changes in matter or in conditions that may lead to such changes.
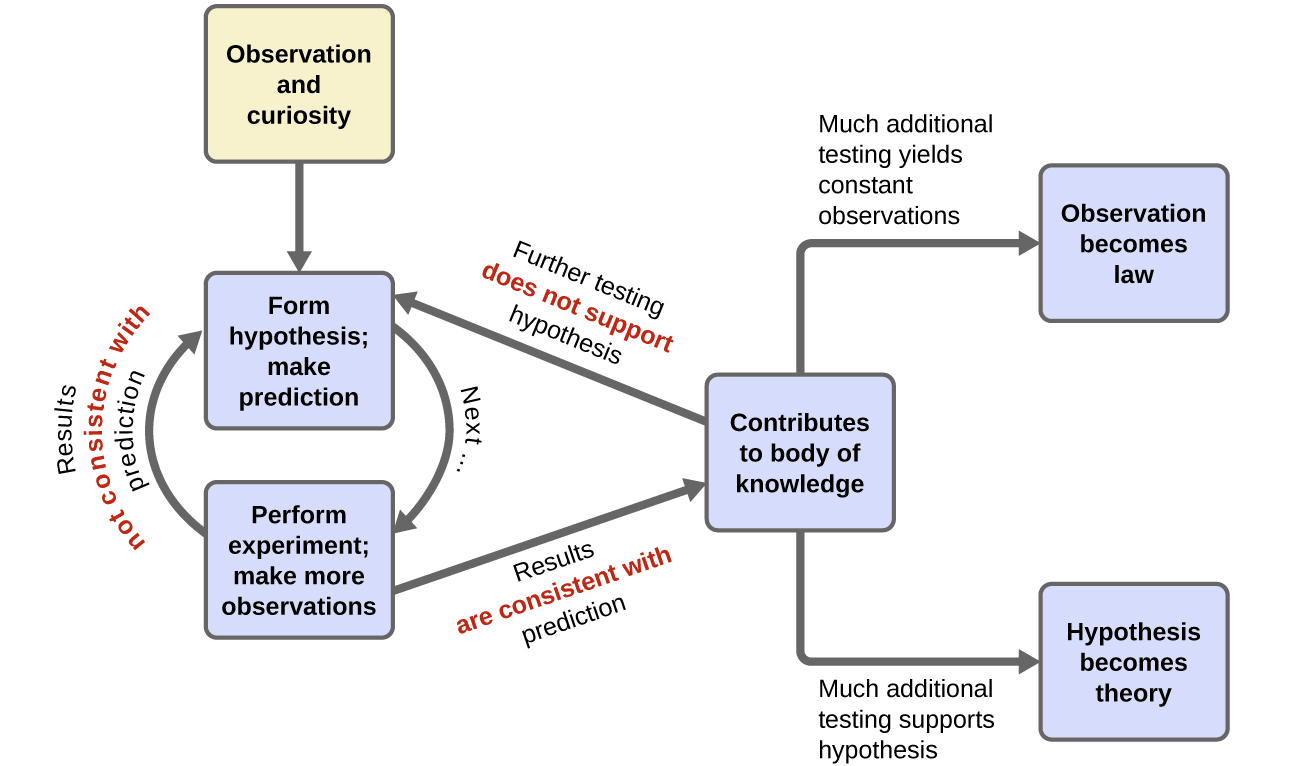
Chemistry is a science based on observation and experimentation. Doing chemistry involves attempting to answer questions and explain observations in terms of the laws and theories of chemistry, using procedures that are accepted by the scientific community. There is no single route to answering a question or explaining an observation, but there is an aspect common to every approach: Each uses knowledge based on experiments that can be reproduced to verify the results. Some routes involve a hypothesis , a tentative explanation of observations that acts as a guide for gathering and checking information. We test a hypothesis by experimentation, calculation, and/or comparison with the experiments of others and then refine it as needed.
Some hypotheses are attempts to explain the behavior that is summarized in laws. The laws of science summarize a vast number of experimental observations, and describe or predict some facet of the natural world. If such a hypothesis turns out to be capable of explaining a large body of experimental data, it can reach the status of a theory. Scientific theories are well-substantiated, comprehensive, testable explanations of particular aspects of nature. Theories are accepted because they provide satisfactory explanations, but they can be modified if new data become available. The path of discovery that leads from question and observation to law or hypothesis to theory, combined with experimental verification of the hypothesis and any necessary modification of the theory, is called the scientific method ( [link] ).
Chemists study and describe the behavior of matter and energy in three different domains: macroscopic, microscopic, and symbolic. These domains provide different ways of considering and describing chemical behavior.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?