| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
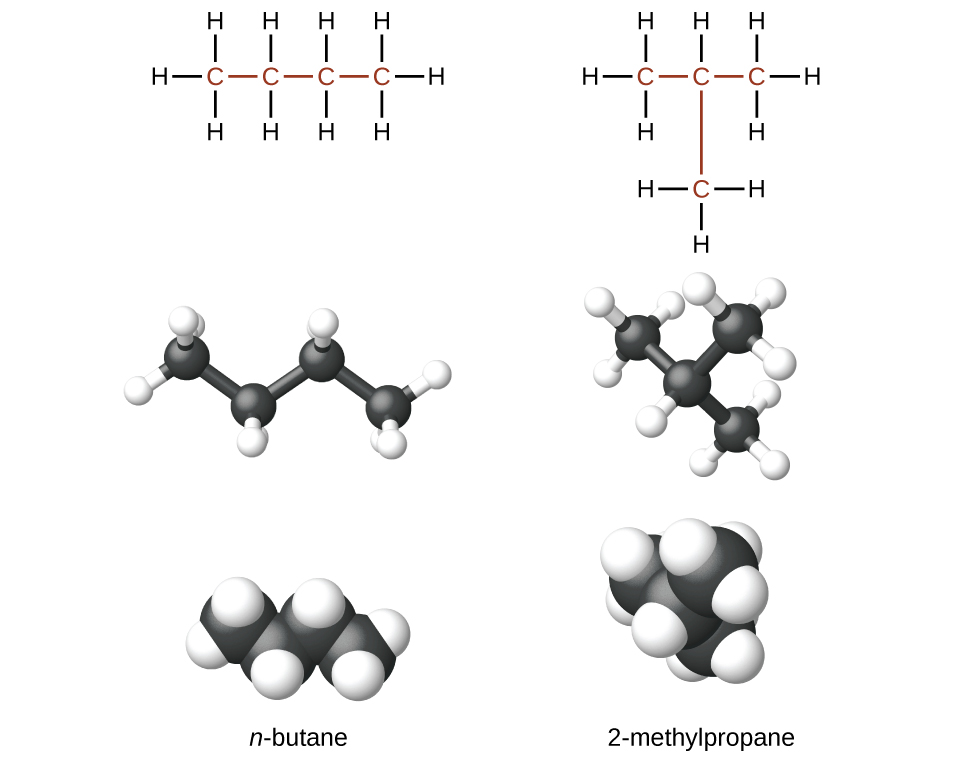
The compounds n -butane and 2-methylpropane are structural isomers (the term constitutional isomers is also commonly used). Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangements of the atoms in their molecules. The n -butane molecule contains an unbranched chain , meaning that no carbon atom is bonded to more than two other carbon atoms. We use the term normal , or the prefix n , to refer to a chain of carbon atoms without branching. The compound 2–methylpropane has a branched chain (the carbon atom in the center of the Lewis structure is bonded to three other carbon atoms)
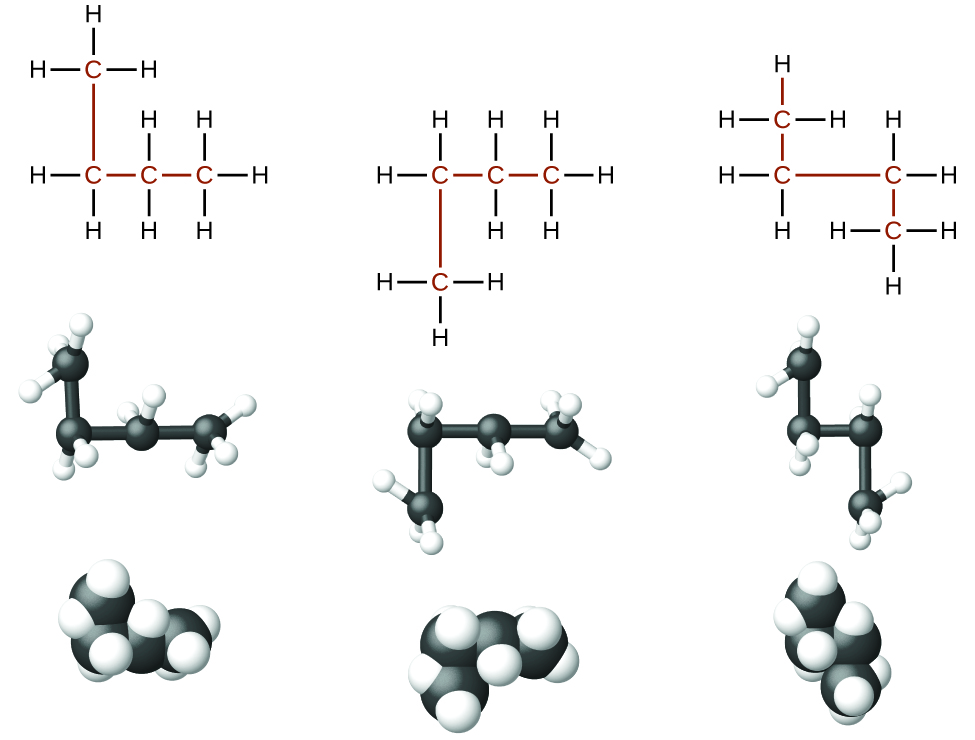
Identifying isomers from Lewis structures is not as easy as it looks. Lewis structures that look different may actually represent the same isomers. For example, the three structures in [link] all represent the same molecule, n -butane, and hence are not different isomers. They are identical because each contains an unbranched chain of four carbon atoms.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ( IUPAC ) has devised a system of nomenclature that begins with the names of the alkanes and can be adjusted from there to account for more complicated structures. The nomenclature for alkanes is based on two rules:
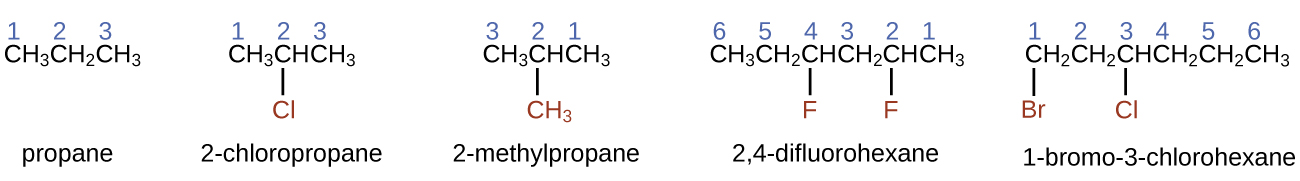
When more than one substituent is present, either on the same carbon atom or on different carbon atoms, the substituents are listed alphabetically. Because the carbon atom numbering begins at the end closest to a substituent, the longest chain of carbon atoms is numbered in such a way as to produce the lowest number for the substituents. The ending -o replaces -ide at the end of the name of an electronegative substituent (in ionic compounds, the negatively charged ion ends with -ide like chloride; in organic compounds, such atoms are treated as substituents and the -o ending is used). The number of substituents of the same type is indicated by the prefixes di- (two), tri- (three), tetra- (four), and so on (for example, difluoro- indicates two fluoride substituents).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?