| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Green plants continually replenish the oxygen in the atmosphere by a process called photosynthesis . The products of photosynthesis may vary, but, in general, the process converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar) and oxygen using the energy of light:
Thus, the oxygen that became carbon dioxide and water by the metabolic processes in plants and animals returns to the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
When dry oxygen is passed between two electrically charged plates, ozone (O 3 , illustrated in [link] ), an allotrope of oxygen possessing a distinctive odor, forms. The formation of ozone from oxygen is an endothermic reaction, in which the energy comes from an electrical discharge, heat, or ultraviolet light:
The sharp odor associated with sparking electrical equipment is due, in part, to ozone.
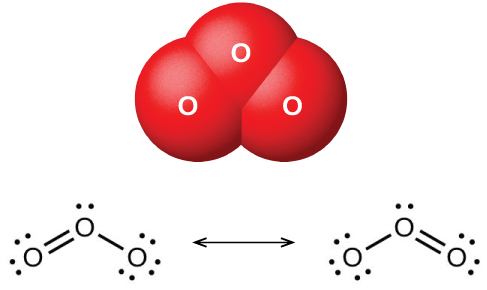
Ozone forms naturally in the upper atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet light from the sun on the oxygen there. Most atmospheric ozone occurs in the stratosphere, a layer of the atmosphere extending from about 10 to 50 kilometers above the earth’s surface. This ozone acts as a barrier to harmful ultraviolet light from the sun by absorbing it via a chemical decomposition reaction:
The reactive oxygen atoms recombine with molecular oxygen to complete the ozone cycle. The presence of stratospheric ozone decreases the frequency of skin cancer and other damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation. It has been clearly demonstrated that chlorofluorocarbons, CFCs (known commercially as Freons), which were present as aerosol propellants in spray cans and as refrigerants, caused depletion of ozone in the stratosphere. This occurred because ultraviolet light also causes CFCs to decompose, producing atomic chlorine. The chlorine atoms react with ozone molecules, resulting in a net removal of O 3 molecules from stratosphere. This process is explored in detail in our coverage of chemical kinetics. There is a worldwide effort to reduce the amount of CFCs used commercially, and the ozone hole is already beginning to decrease in size as atmospheric concentrations of atomic chlorine decrease. While ozone in the stratosphere helps protect us, ozone in the troposphere is a problem. This ozone is a toxic component of photochemical smog.
The uses of ozone depend on its reactivity with other substances. It can be used as a bleaching agent for oils, waxes, fabrics, and starch: It oxidizes the colored compounds in these substances to colorless compounds. It is an alternative to chlorine as a disinfectant for water.
Elemental oxygen is a strong oxidizing agent. It reacts with most other elements and many compounds.
Oxygen reacts directly at room temperature or at elevated temperatures with all other elements except the noble gases, the halogens, and few second- and third-row transition metals of low reactivity (those with higher reduction potentials than copper). Rust is an example of the reaction of oxygen with iron. The more active metals form peroxides or superoxides. Less active metals and the nonmetals give oxides. Two examples of these reactions are:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?