| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When a central atom has two lone electron pairs and four bonding regions, we have an octahedral electron-pair geometry. The two lone pairs are on opposite sides of the octahedron (180° apart), giving a square planar molecular structure that minimizes lone pair-lone pair repulsions ( [link] ).
The following procedure uses VSEPR theory to determine the electron pair geometries and the molecular structures:
The following examples illustrate the use of VSEPR theory to predict the molecular structure of molecules or ions that have no lone pairs of electrons. In this case, the molecular structure is identical to the electron pair geometry.
(a) carbon dioxide, CO 2 , a molecule produced by the combustion of fossil fuels
(b) boron trichloride, BCl 3 , an important industrial chemical
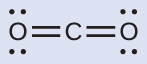
This shows us two regions of high electron density around the carbon atom—each double bond counts as one region, and there are no lone pairs on the carbon atom. Using VSEPR theory, we predict that the two regions of electron density arrange themselves on opposite sides of the central atom with a bond angle of 180°. The electron-pair geometry and molecular structure are identical, and CO 2 molecules are linear.
(b) We write the Lewis structure of BCl 3 as:
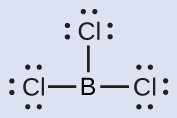
Thus we see that BCl 3 contains three bonds, and there are no lone pairs of electrons on boron. The arrangement of three regions of high electron density gives a trigonal planar electron-pair geometry. The B–Cl bonds lie in a plane with 120° angles between them. BCl 3 also has a trigonal planar molecular structure ( [link] ).
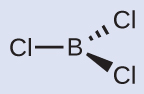
The electron-pair geometry and molecular structure of BCl 3 are both trigonal planar. Note that the VSEPR geometry indicates the correct bond angles (120°), unlike the Lewis structure shown above.
The electron-pair geometry is trigonal planar and the molecular structure is trigonal planar. Due to resonance, all three C–O bonds are identical. Whether they are single, double, or an average of the two, each bond counts as one region of electron density.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?