| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most nonmetals react with oxygen to form nonmetal oxides. Depending on the available oxidation states for the element, a variety of oxides might form. Fluorine will combine with oxygen to form fluorides such as OF 2 , where the oxygen has a 2+-oxidation state.
The two common oxides of sulfur are sulfur dioxide, SO 2 , and sulfur trioxide, SO 3 . The odor of burning sulfur comes from sulfur dioxide. Sulfur dioxide, shown in [link] , occurs in volcanic gases and in the atmosphere near industrial plants that burn fuel containing sulfur compounds.
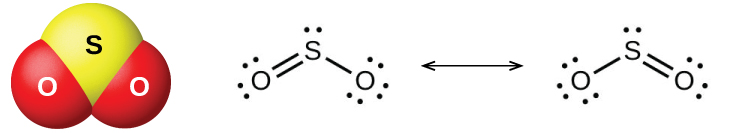
Commercial production of sulfur dioxide is from either burning sulfur or roasting sulfide ores such as ZnS, FeS 2 , and Cu 2 S in air. (Roasting, which forms the metal oxide, is the first step in the separation of many metals from their ores.) A convenient method for preparing sulfur dioxide in the laboratory is by the action of a strong acid on either sulfite salts containing the ion or hydrogen sulfite salts containing Sulfurous acid, H 2 SO 3 , forms first, but quickly decomposes into sulfur dioxide and water. Sulfur dioxide also forms when many reducing agents react with hot, concentrated sulfuric acid. Sulfur trioxide forms slowly when heating sulfur dioxide and oxygen together, and the reaction is exothermic:
Sulfur dioxide is a gas at room temperature, and the SO 2 molecule is bent. Sulfur trioxide melts at 17 °C and boils at 43 °C. In the vapor state, its molecules are single SO 3 units (shown in [link] ), but in the solid state, SO 3 exists in several polymeric forms.
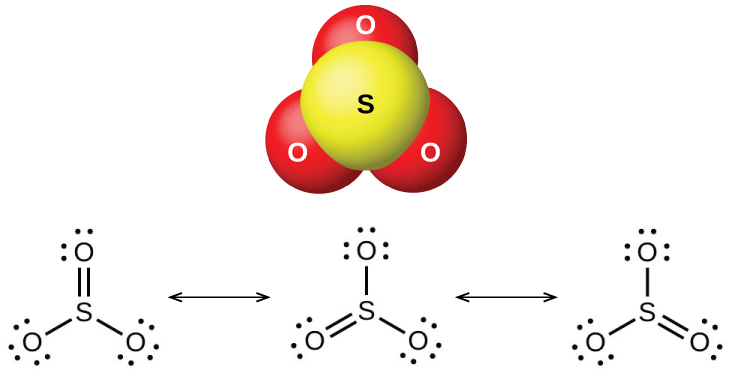
The sulfur oxides react as Lewis acids with many oxides and hydroxides in Lewis acid-base reactions, with the formation of sulfites or hydrogen sulfites , and sulfates or hydrogen sulfates , respectively.
The halogens do not react directly with oxygen, but it is possible to prepare binary oxygen-halogen compounds by the reactions of the halogens with oxygen-containing compounds. Oxygen compounds with chlorine, bromine, and iodine are oxides because oxygen is the more electronegative element in these compounds. On the other hand, fluorine compounds with oxygen are fluorides because fluorine is the more electronegative element.
As a class, the oxides are extremely reactive and unstable, and their chemistry has little practical importance. Dichlorine oxide, formally called dichlorine monoxide, and chlorine dioxide, both shown in [link] , are the only commercially important compounds. They are important as bleaching agents (for use with pulp and flour) and for water treatment.
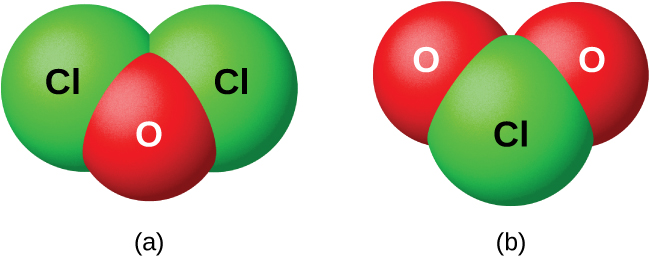
Nonmetal oxides form acids when allowed to react with water; these are acid anhydrides. The resulting oxyanions can form salts with various metal ions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?