| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
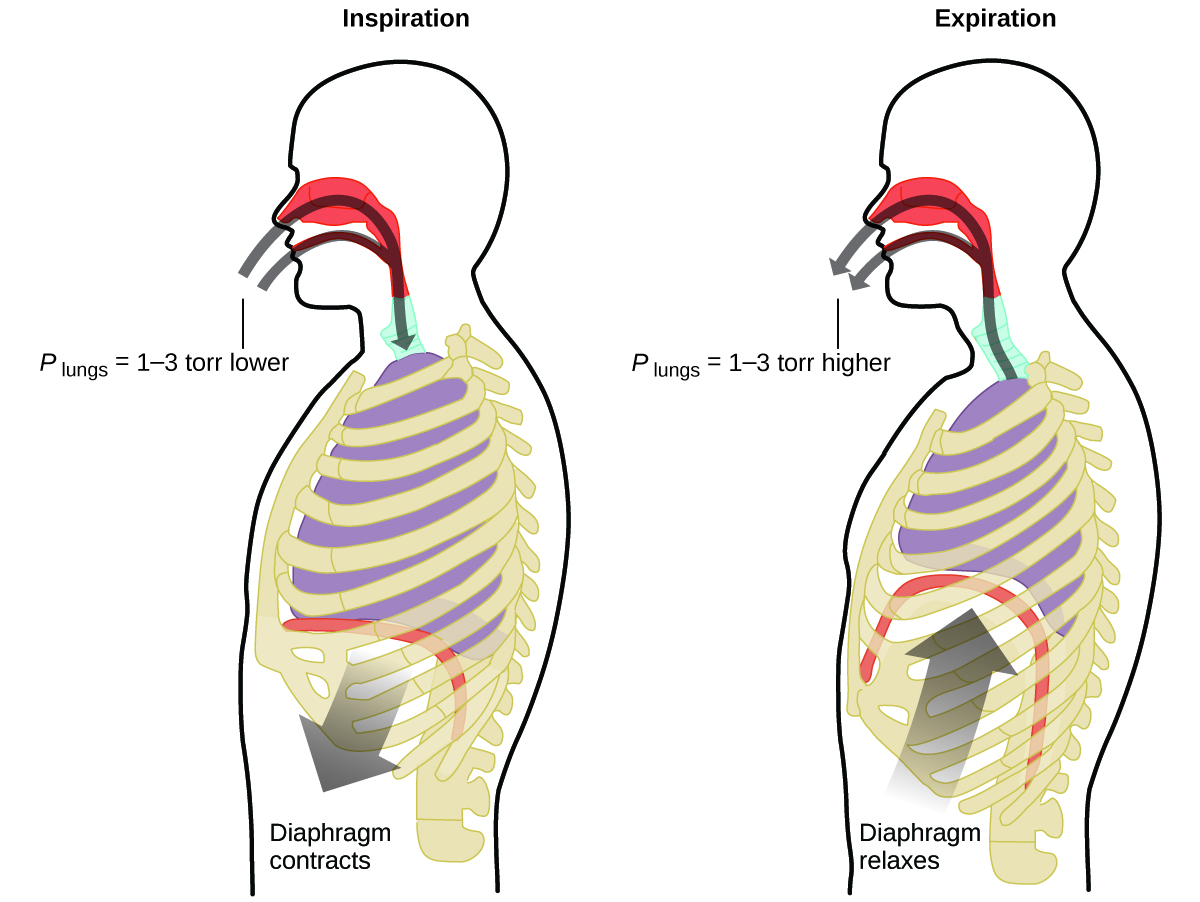
What do you do about 20 times per minute for your whole life, without break, and often without even being aware of it? The answer, of course, is respiration, or breathing. How does it work? It turns out that the gas laws apply here. Your lungs take in gas that your body needs (oxygen) and get rid of waste gas (carbon dioxide). Lungs are made of spongy, stretchy tissue that expands and contracts while you breathe. When you inhale, your diaphragm and intercostal muscles (the muscles between your ribs) contract, expanding your chest cavity and making your lung volume larger. The increase in volume leads to a decrease in pressure (Boyle’s law). This causes air to flow into the lungs (from high pressure to low pressure). When you exhale, the process reverses: Your diaphragm and rib muscles relax, your chest cavity contracts, and your lung volume decreases, causing the pressure to increase (Boyle’s law again), and air flows out of the lungs (from high pressure to low pressure). You then breathe in and out again, and again, repeating this Boyle’s law cycle for the rest of your life ( [link] ).
The Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro advanced a hypothesis in 1811 to account for the behavior of gases, stating that equal volumes of all gases, measured under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, contain the same number of molecules. Over time, this relationship was supported by many experimental observations as expressed by Avogadro’s law : For a confined gas, the volume (V) and number of moles (n) are directly proportional if the pressure and temperature both remain constant .
In equation form, this is written as:
Mathematical relationships can also be determined for the other variable pairs, such as P versus n , and n versus T .
Visit this interactive PhET simulation to investigate the relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas. Use the simulation to examine the effect of changing one parameter on another while holding the other parameters constant (as described in the preceding sections on the various gas laws).
To this point, four separate laws have been discussed that relate pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of the gas:
Combining these four laws yields the ideal gas law , a relation between the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas:
where P is the pressure of a gas, V is its volume, n is the number of moles of the gas, T is its temperature on the kelvin scale, and R is a constant called the ideal gas constant or the universal gas constant. The units used to express pressure, volume, and temperature will determine the proper form of the gas constant as required by dimensional analysis, the most commonly encountered values being 0.08206 L atm mol –1 K –1 and 8.314 kPa L mol –1 K –1 .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?