| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
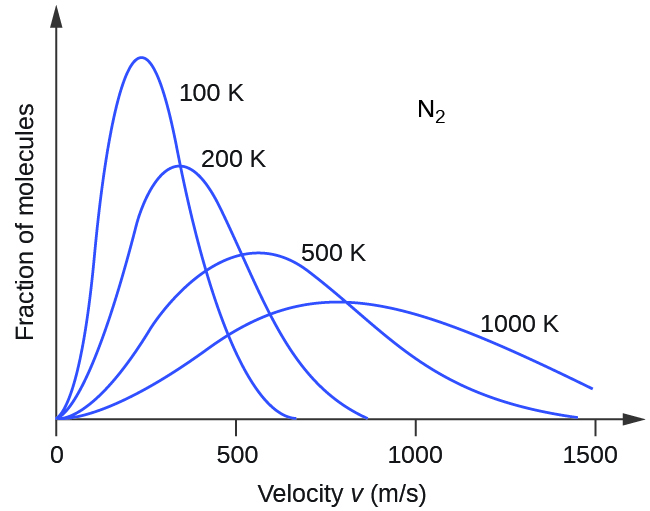
If the temperature of a gas increases, its KE avg increases, more molecules have higher speeds and fewer molecules have lower speeds, and the distribution shifts toward higher speeds overall, that is, to the right. If temperature decreases, KE avg decreases, more molecules have lower speeds and fewer molecules have higher speeds, and the distribution shifts toward lower speeds overall, that is, to the left. This behavior is illustrated for nitrogen gas in [link] .
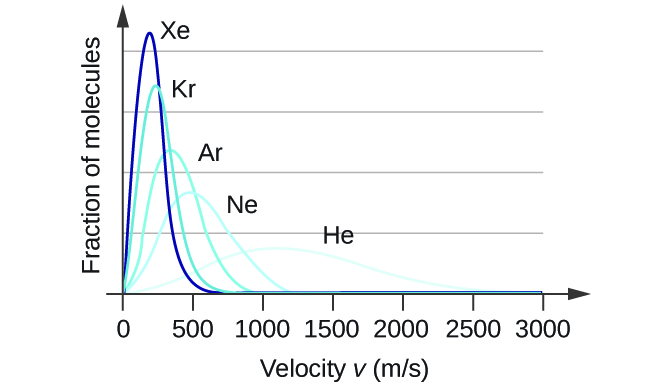
At a given temperature, all gases have the same KE avg for their molecules. Gases composed of lighter molecules have more high-speed particles and a higher u rms , with a speed distribution that peaks at relatively higher velocities. Gases consisting of heavier molecules have more low-speed particles, a lower u rms , and a speed distribution that peaks at relatively lower velocities. This trend is demonstrated by the data for a series of noble gases shown in [link] .
The gas simulator may be used to examine the effect of temperature on molecular velocities. Examine the simulator’s “energy histograms” (molecular speed distributions) and “species information” (which gives average speed values) for molecules of different masses at various temperatures.
According to Graham’s law, the molecules of a gas are in rapid motion and the molecules themselves are small. The average distance between the molecules of a gas is large compared to the size of the molecules. As a consequence, gas molecules can move past each other easily and diffuse at relatively fast rates.
The rate of effusion of a gas depends directly on the (average) speed of its molecules:
Using this relation, and the equation relating molecular speed to mass, Graham’s law may be easily derived as shown here:
The ratio of the rates of effusion is thus derived to be inversely proportional to the ratio of the square roots of their masses. This is the same relation observed experimentally and expressed as Graham’s law.
The kinetic molecular theory is a simple but very effective model that effectively explains ideal gas behavior. The theory assumes that gases consist of widely separated molecules of negligible volume that are in constant motion, colliding elastically with one another and the walls of their container with average velocities determined by their absolute temperatures. The individual molecules of a gas exhibit a range of velocities, the distribution of these velocities being dependent on the temperature of the gas and the mass of its molecules.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?