| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Hydroxy compounds of elements with intermediate electronegativities and relatively high oxidation numbers (for example, elements near the diagonal line separating the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table) are usually amphoteric. This means that the hydroxy compounds act as acids when they react with strong bases and as bases when they react with strong acids. The amphoterism of aluminum hydroxide, which commonly exists as the hydrate Al(H 2 O) 3 (OH) 3 , is reflected in its solubility in both strong acids and strong bases. In strong bases, the relatively insoluble hydrated aluminum hydroxide, Al(H 2 O) 3 (OH) 3 , is converted into the soluble ion, by reaction with hydroxide ion:
In this reaction, a proton is transferred from one of the aluminum-bound H 2 O molecules to a hydroxide ion in solution. The Al(H 2 O) 3 (OH) 3 compound thus acts as an acid under these conditions. On the other hand, when dissolved in strong acids, it is converted to the soluble ion by reaction with hydronium ion:
In this case, protons are transferred from hydronium ions in solution to Al(H 2 O) 3 (OH) 3 , and the compound functions as a base.
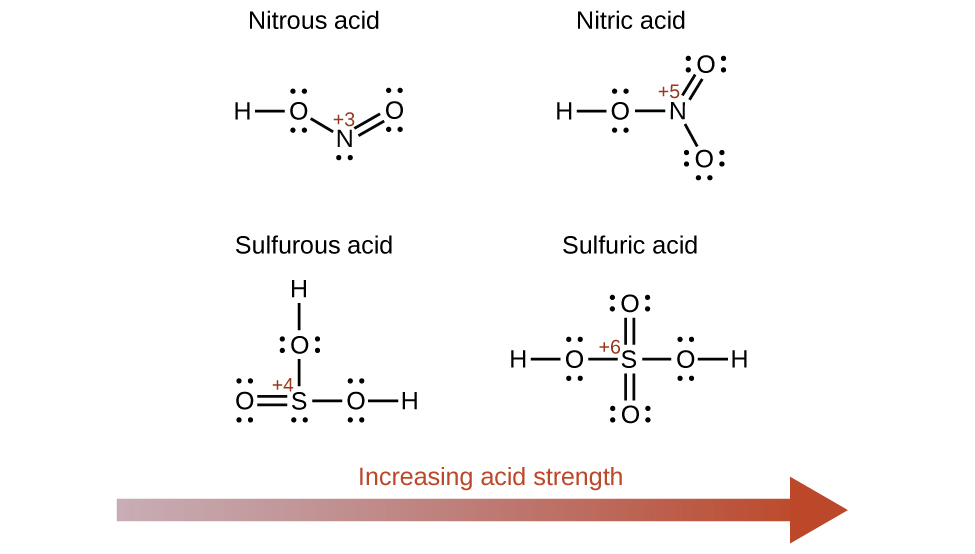
The strengths of Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases in aqueous solutions can be determined by their acid or base ionization constants. Stronger acids form weaker conjugate bases, and weaker acids form stronger conjugate bases. Thus strong acids are completely ionized in aqueous solution because their conjugate bases are weaker bases than water. Weak acids are only partially ionized because their conjugate bases are strong enough to compete successfully with water for possession of protons. Strong bases react with water to quantitatively form hydroxide ions. Weak bases give only small amounts of hydroxide ion. The strengths of the binary acids increase from left to right across a period of the periodic table (CH 4 <NH 3 <H 2 O<HF), and they increase down a group (HF<HCl<HBr<HI). The strengths of oxyacids that contain the same central element increase as the oxidation number of the element increases (H 2 SO 3 <H 2 SO 4 ). The strengths of oxyacids also increase as the electronegativity of the central element increases [H 2 SeO 4 <H 2 SO 4 ].
Explain why the neutralization reaction of a strong acid and a weak base gives a weakly acidic solution.
Explain why the neutralization reaction of a weak acid and a strong base gives a weakly basic solution.
The salt ionizes in solution, but the anion slightly reacts with water to form the weak acid. This reaction also forms OH − , which causes the solution to be basic.
Use this list of important industrial compounds (and [link] ) to answer the following questions regarding: CaO, Ca(OH) 2 , CH 3 CO 2 H, CO 2, HCl, H 2 CO 3 , HF, HNO 2 , HNO 3 , H 3 PO 4 , H 2 SO 4 , NH 3 , NaOH, Na 2 CO 3 .
(a) Identify the strong Brønsted-Lowry acids and strong Brønsted-Lowry bases.
(b) List those compounds in (a) that can behave as Brønsted-Lowry acids with strengths lying between those of H 3 O + and H 2 O.
(c) List those compounds in (a) that can behave as Brønsted-Lowry bases with strengths lying between those of H 2 O and OH − .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?