| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
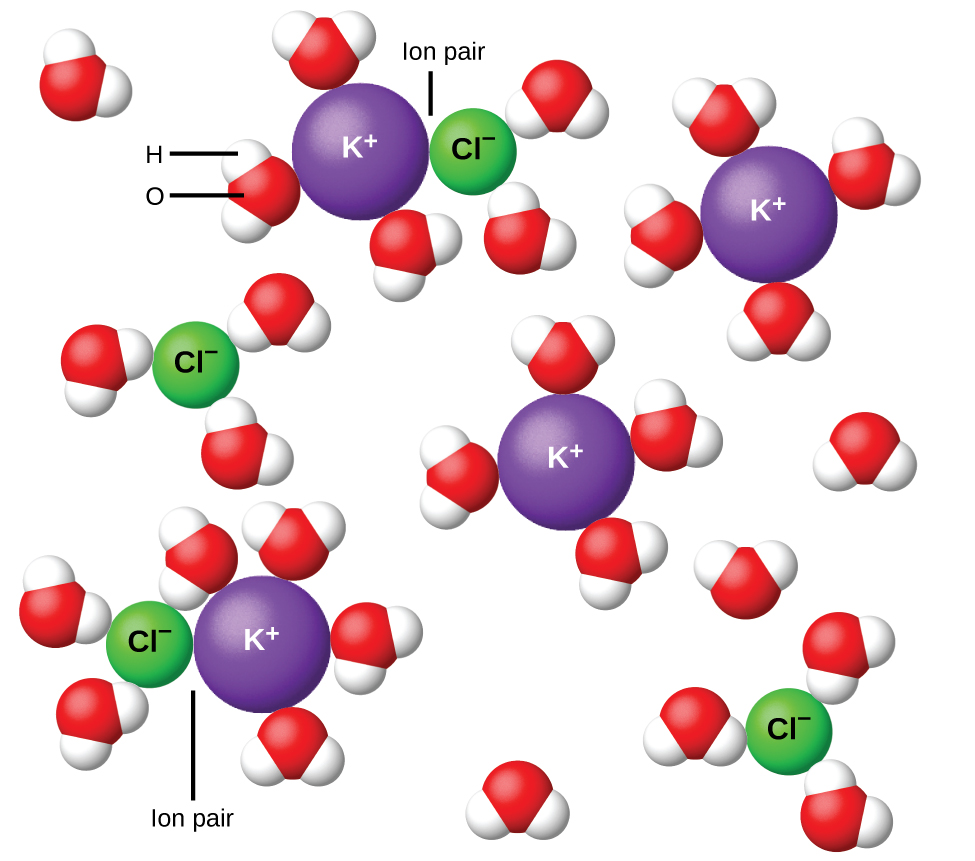
In 1923, the chemists Peter Debye and Erich Hückel proposed a theory to explain the apparent incomplete ionization of strong electrolytes. They suggested that although interionic attraction in an aqueous solution is very greatly reduced by solvation of the ions and the insulating action of the polar solvent, it is not completely nullified. The residual attractions prevent the ions from behaving as totally independent particles ( [link] ). In some cases, a positive and negative ion may actually touch, giving a solvated unit called an ion pair. Thus, the activity , or the effective concentration, of any particular kind of ion is less than that indicated by the actual concentration. Ions become more and more widely separated the more dilute the solution, and the residual interionic attractions become less and less. Thus, in extremely dilute solutions, the effective concentrations of the ions (their activities) are essentially equal to the actual concentrations. Note that the van’t Hoff factors for the electrolytes in [link] are for 0.05 m solutions, at which concentration the value of i for NaCl is 1.9, as opposed to an ideal value of 2.
Properties of a solution that depend only on the concentration of solute particles are called colligative properties. They include changes in the vapor pressure, boiling point, and freezing point of the solvent in the solution. The magnitudes of these properties depend only on the total concentration of solute particles in solution, not on the type of particles. The total concentration of solute particles in a solution also determines its osmotic pressure. This is the pressure that must be applied to the solution to prevent diffusion of molecules of pure solvent through a semipermeable membrane into the solution. Ionic compounds may not completely dissociate in solution due to activity effects, in which case observed colligative effects may be less than predicted.
Which is/are part of the macroscopic domain of solutions and which is/are part of the microscopic domain: boiling point elevation, Henry’s law, hydrogen bond, ion-dipole attraction, molarity, nonelectrolyte, nonstoichiometric compound, osmosis, solvated ion?
What is the microscopic explanation for the macroscopic behavior illustrated in [link] ?
The strength of the bonds between like molecules is stronger than the strength between unlike molecules. Therefore, some regions will exist in which the water molecules will exclude oil molecules and other regions will exist in which oil molecules will exclude water molecules, forming a heterogeneous region.
Sketch a qualitative graph of the pressure versus time for water vapor above a sample of pure water and a sugar solution, as the liquids evaporate to half their original volume.
A solution of potassium nitrate, an electrolyte, and a solution of glycerin (C 3 H 5 (OH) 3 ), a nonelectrolyte, both boil at 100.3 °C. What other physical properties of the two solutions are identical?
Both form homogeneous solutions; their boiling point elevations are the same, as are their lowering of vapor pressures. Osmotic pressure and the lowering of the freezing point are also the same for both solutions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?