| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. The sun and other stars are composed largely of hydrogen. Astronomers estimate that 90% of the atoms in the universe are hydrogen atoms. Hydrogen is a component of more compounds than any other element. Water is the most abundant compound of hydrogen found on earth. Hydrogen is an important part of petroleum, many minerals, cellulose and starch, sugar, fats, oils, alcohols, acids, and thousands of other substances.
At ordinary temperatures, hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and nonpoisonous gas consisting of the diatomic molecule H 2 . Hydrogen is composed of three isotopes, and unlike other elements, these isotopes have different names and chemical symbols: protium, 1 H, deuterium, 2 H (or “D”), and tritium 3 H (or “T”). In a naturally occurring sample of hydrogen, there is one atom of deuterium for every 7000 H atoms and one atom of radioactive tritium for every 10 18 H atoms. The chemical properties of the different isotopes are very similar because they have identical electron structures, but they differ in some physical properties because of their differing atomic masses. Elemental deuterium and tritium have lower vapor pressure than ordinary hydrogen. Consequently, when liquid hydrogen evaporates, the heavier isotopes are concentrated in the last portions to evaporate. Electrolysis of heavy water, D 2 O, yields deuterium. Most tritium originates from nuclear reactions.
Elemental hydrogen must be prepared from compounds by breaking chemical bonds. The most common methods of preparing hydrogen follow.
Water is the cheapest and most abundant source of hydrogen. Passing steam over coke (an impure form of elemental carbon) at 1000 °C produces a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen known as water gas:
Water gas is as an industrial fuel. It is possible to produce additional hydrogen by mixing the water gas with steam in the presence of a catalyst to convert the CO to CO 2 . This reaction is the water gas shift reaction.
It is also possible to prepare a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide by passing hydrocarbons from natural gas or petroleum and steam over a nickel-based catalyst. Propane is an example of a hydrocarbon reactant:
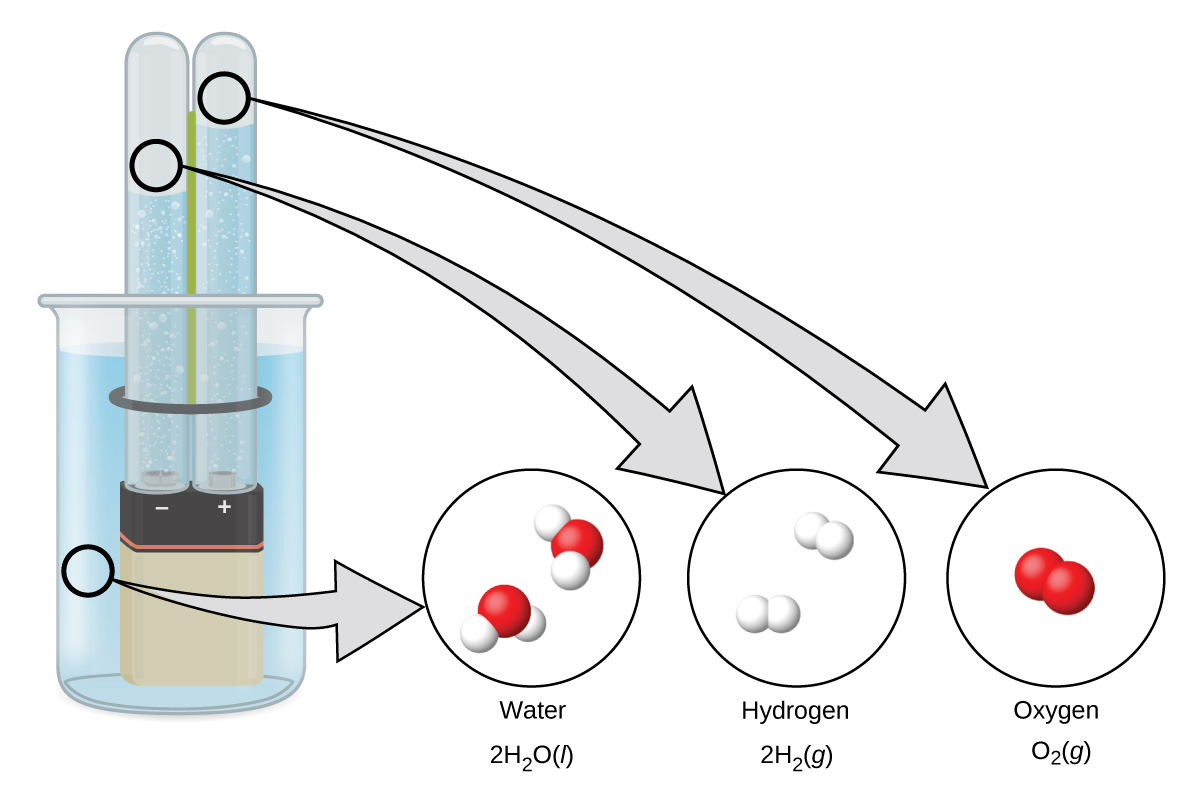
Hydrogen forms when direct current electricity passes through water containing an electrolyte such as H 2 SO 4 , as illustrated in [link] . Bubbles of hydrogen form at the cathode, and oxygen evolves at the anode. The net reaction is:
This is the most convenient laboratory method of producing hydrogen. Metals with lower reduction potentials reduce the hydrogen ion in dilute acids to produce hydrogen gas and metal salts. For example, as shown in [link] , iron in dilute hydrochloric acid produces hydrogen gas and iron(II) chloride:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?