| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can also liquefy many gases by compressing them, if the temperature is not too high. The increased pressure brings the molecules of a gas closer together, such that the attractions between the molecules become strong relative to their KE. Consequently, they form liquids. Butane, C 4 H 10 , is the fuel used in disposable lighters and is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. Inside the lighter’s fuel compartment, the butane is compressed to a pressure that results in its condensation to the liquid state, as shown in [link] .

Finally, if the temperature of a liquid becomes sufficiently low, or the pressure on the liquid becomes sufficiently high, the molecules of the liquid no longer have enough KE to overcome the IMF between them, and a solid forms. A more thorough discussion of these and other changes of state, or phase transitions, is provided in a later module of this chapter.
Access this interactive simulation on states of matter, phase transitions, and intermolecular forces. This simulation is useful for visualizing concepts introduced throughout this chapter.
Under appropriate conditions, the attractions between all gas molecules will cause them to form liquids or solids. This is due to intermolecular forces, not intra molecular forces. Intra molecular forces are those within the molecule that keep the molecule together, for example, the bonds between the atoms. Inter molecular forces are the attractions between molecules, which determine many of the physical properties of a substance. [link] illustrates these different molecular forces. The strengths of these attractive forces vary widely, though usually the IMFs between small molecules are weak compared to the intramolecular forces that bond atoms together within a molecule. For example, to overcome the IMFs in one mole of liquid HCl and convert it into gaseous HCl requires only about 17 kilojoules. However, to break the covalent bonds between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms in one mole of HCl requires about 25 times more energy—430 kilojoules.
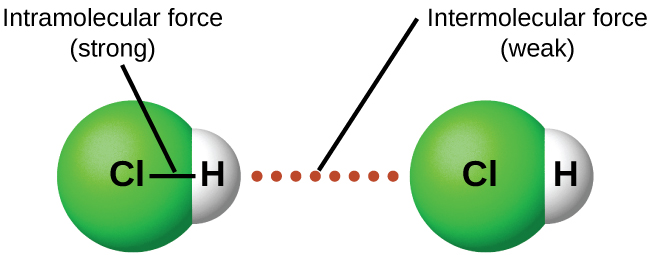
All of the attractive forces between neutral atoms and molecules are known as van der Waals forces , although they are usually referred to more informally as intermolecular attraction. We will consider the various types of IMFs in the next three sections of this module.
One of the three van der Waals forces is present in all condensed phases, regardless of the nature of the atoms or molecules composing the substance. This attractive force is called the London dispersion force in honor of German-born American physicist Fritz London who, in 1928, first explained it. This force is often referred to as simply the dispersion force . Because the electrons of an atom or molecule are in constant motion (or, alternatively, the electron’s location is subject to quantum-mechanical variability), at any moment in time, an atom or molecule can develop a temporary, instantaneous dipole if its electrons are distributed asymmetrically. The presence of this dipole can, in turn, distort the electrons of a neighboring atom or molecule, producing an induced dipole . These two rapidly fluctuating, temporary dipoles thus result in a relatively weak electrostatic attraction between the species—a so-called dispersion force like that illustrated in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?