| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
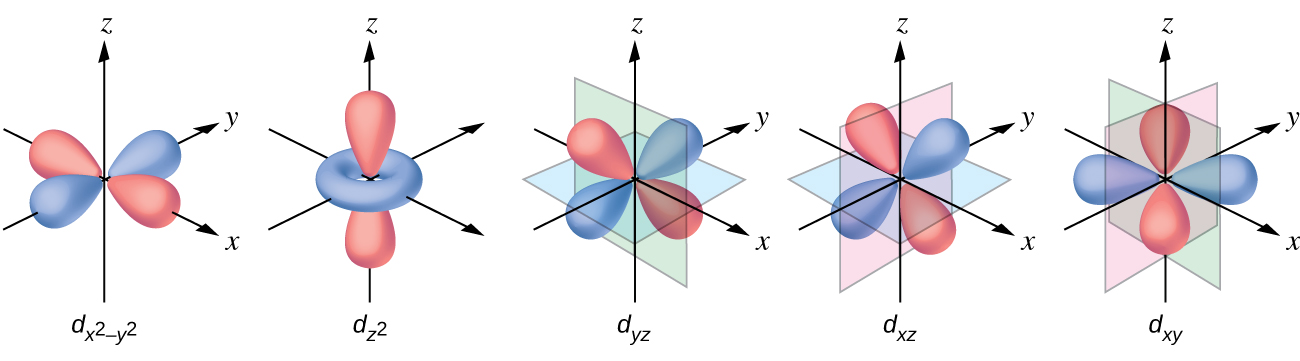
The other common geometry is square planar. It is possible to consider a square planar geometry as an octahedral structure with a pair of trans ligands removed. The removed ligands are assumed to be on the z -axis. This changes the distribution of the d orbitals, as orbitals on or near the z -axis become more stable, and those on or near the x- or y -axes become less stable. This results in the octahedral t 2 g and the e g sets splitting and gives a more complicated pattern with no simple Δ oct . The basic pattern is:
Experimental evidence of magnetic measurements supports the theory of high- and low-spin complexes. Remember that molecules such as O 2 that contain unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. Paramagnetic substances are attracted to magnetic fields. Many transition metal complexes have unpaired electrons and hence are paramagnetic. Molecules such as N 2 and ions such as Na + and [Fe(CN) 6 ] 4− that contain no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic. Diamagnetic substances have a slight tendency to be repelled by magnetic fields.
When an electron in an atom or ion is unpaired, the magnetic moment due to its spin makes the entire atom or ion paramagnetic. The size of the magnetic moment of a system containing unpaired electrons is related directly to the number of such electrons: the greater the number of unpaired electrons, the larger the magnetic moment. Therefore, the observed magnetic moment is used to determine the number of unpaired electrons present. The measured magnetic moment of low-spin d 6 [Fe(CN) 6 ] 4− confirms that iron is diamagnetic, whereas high-spin d 6 [Fe(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+ has four unpaired electrons with a magnetic moment that confirms this arrangement.
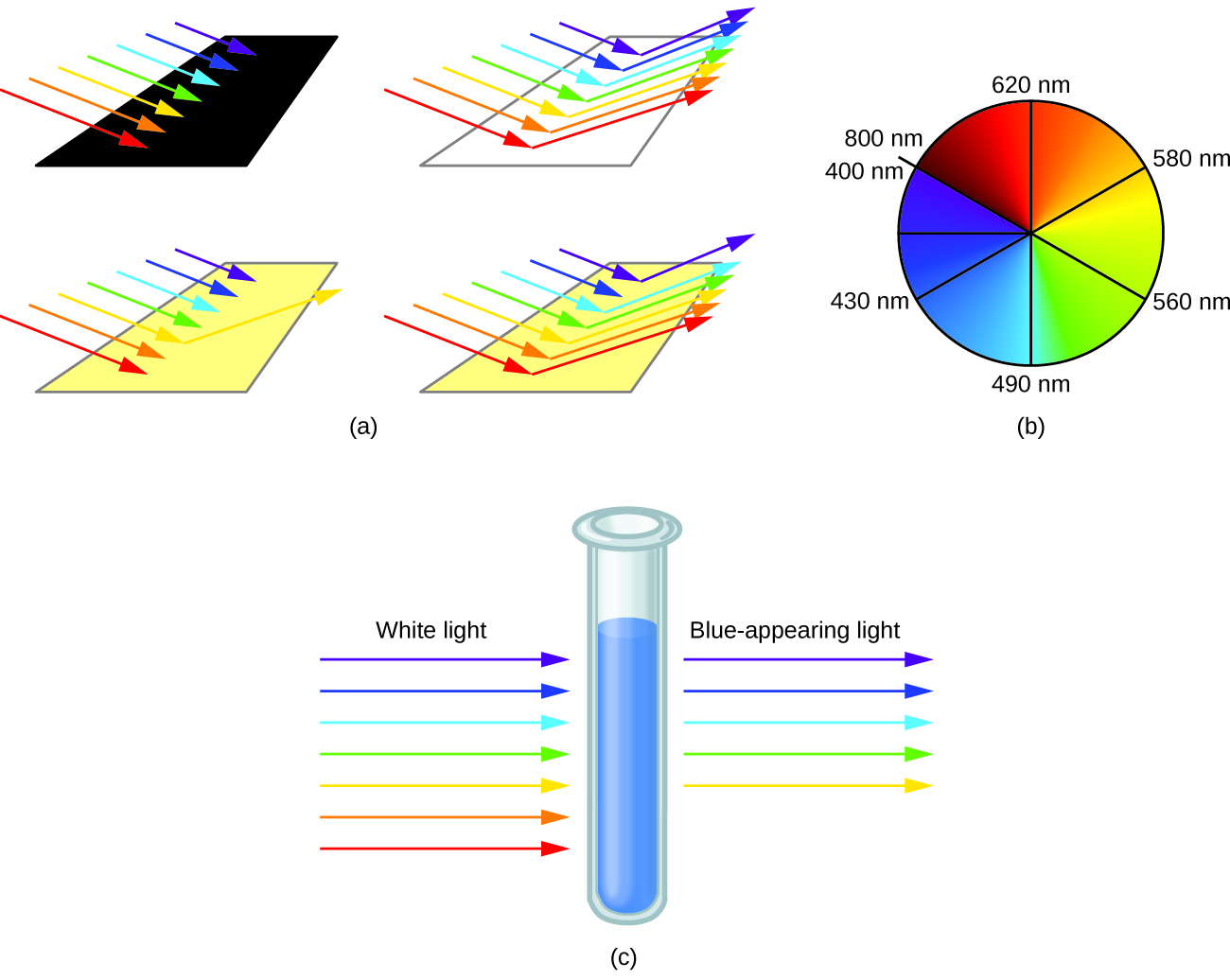
When atoms or molecules absorb light at the proper frequency, their electrons are excited to higher-energy orbitals. For many main group atoms and molecules, the absorbed photons are in the ultraviolet range of the electromagnetic spectrum, which cannot be detected by the human eye. For coordination compounds, the energy difference between the d orbitals often allows photons in the visible range to be absorbed.
The human eye perceives a mixture of all the colors, in the proportions present in sunlight, as white light. Complementary colors, those located across from each other on a color wheel, are also used in color vision. The eye perceives a mixture of two complementary colors, in the proper proportions, as white light. Likewise, when a color is missing from white light, the eye sees its complement. For example, when red photons are absorbed from white light, the eyes see the color green. When violet photons are removed from white light, the eyes see lemon yellow. The blue color of the [Cu(NH 3 ) 4 ] 2+ ion results because this ion absorbs orange and red light, leaving the complementary colors of blue and green ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?