| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If we know the equilibrium constant for a reaction and a set of concentrations of reactants and products that are not at equilibrium , we can calculate the changes in concentrations as the system comes to equilibrium, as well as the new concentrations at equilibrium. The typical procedure can be summarized in four steps.
Determine the direction the reaction proceeds.
The balanced equation for the decomposition of PCl 5 is
Because we have no products initially, Q c = 0 and the reaction will proceed to the right.
Determine the relative changes needed to reach equilibrium, then write the equilibrium concentrations in terms of these changes.
Let us represent the increase in concentration of PCl 3 by the symbol x . The other changes may be written in terms of x by considering the coefficients in the chemical equation.
The changes in concentration and the expressions for the equilibrium concentrations are:
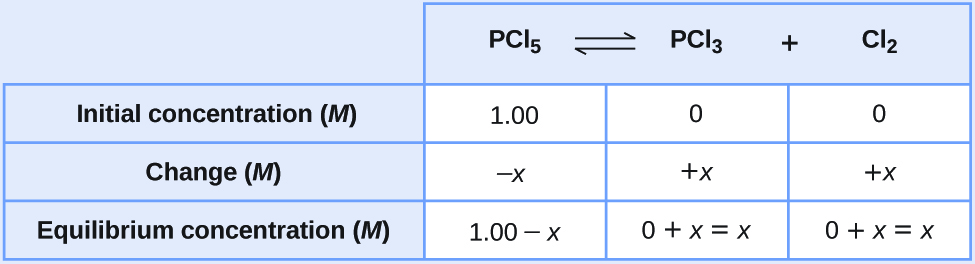
Solve for the change and the equilibrium concentrations.
Substituting the equilibrium concentrations into the equilibrium constant equation gives
This equation contains only one variable, x , the change in concentration. We can write the equation as a quadratic equation and solve for x using the quadratic formula.
Appendix B shows us an equation of the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0 can be rearranged to solve for x :
In this case, a = 1, b = 0.0211, and c = −0.0211. Substituting the appropriate values for a , b , and c yields:
Hence
or
Quadratic equations often have two different solutions, one that is physically possible and one that is physically impossible (an extraneous root). In this case, the second solution (−0.156) is physically impossible because we know the change must be a positive number (otherwise we would end up with negative values for concentrations of the products). Thus, x = 0.135 M .
The equilibrium concentrations are
Check the arithmetic.
Substitution into the expression for K c (to check the calculation) gives
The equilibrium constant calculated from the equilibrium concentrations is equal to the value of K c given in the problem (when rounded to the proper number of significant figures). Thus, the calculated equilibrium concentrations check.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?