| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Hydrocarbon molecules with one or more triple bonds are called alkynes ; they make up another series of unsaturated hydrocarbons. Two carbon atoms joined by a triple bond are bound together by one σ bond and two π bonds. The sp -hybridized carbons involved in the triple bond have bond angles of 180°, giving these types of bonds a linear, rod-like shape.
The simplest member of the alkyne series is ethyne, C 2 H 2 , commonly called acetylene. The Lewis structure for ethyne, a linear molecule, is:
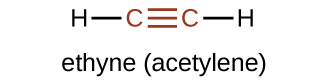
The IUPAC nomenclature for alkynes is similar to that for alkenes except that the suffix -yne is used to indicate a triple bond in the chain. For example, is called 1-butyne.
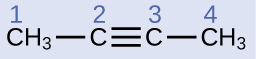
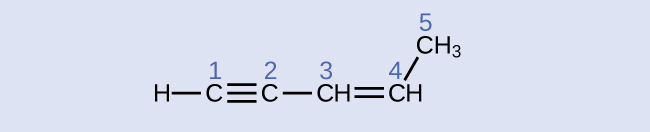
carbon 1: sp , 180°; carbon 2: sp , 180°; carbon 3: sp 2 , 120°; carbon 4: sp 2 , 120°; carbon 5: sp 3 , 109.5°
Chemically, the alkynes are similar to the alkenes. Since the functional group has two π bonds, alkynes typically react even more readily, and react with twice as much reagent in addition reactions. The reaction of acetylene with bromine is a typical example:
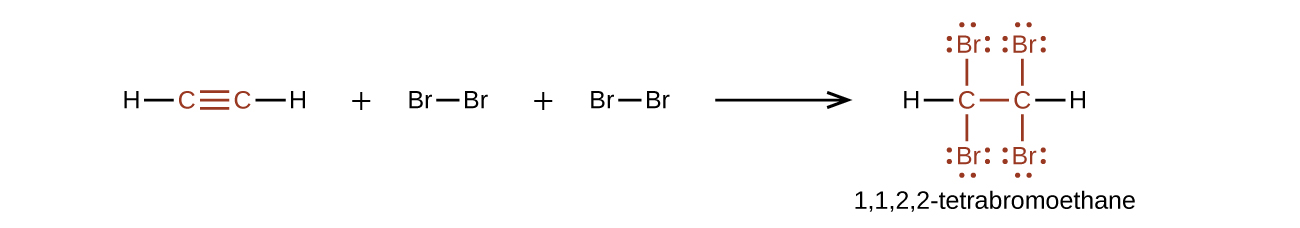
Acetylene and the other alkynes also burn readily. An acetylene torch takes advantage of the high heat of combustion for acetylene.
Benzene, C 6 H 6 , is the simplest member of a large family of hydrocarbons, called aromatic hydrocarbons . These compounds contain ring structures and exhibit bonding that must be described using the resonance hybrid concept of valence bond theory or the delocalization concept of molecular orbital theory. (To review these concepts, refer to the earlier chapters on chemical bonding). The resonance structures for benzene, C 6 H 6 , are:
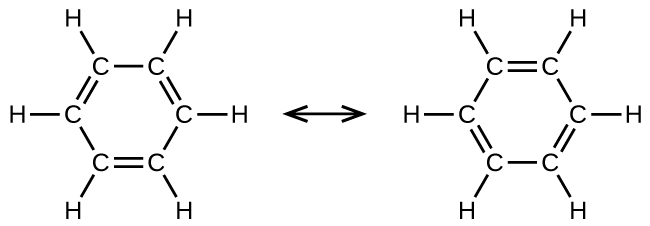
Valence bond theory describes the benzene molecule and other planar aromatic hydrocarbon molecules as hexagonal rings of sp 2 -hybridized carbon atoms with the unhybridized p orbital of each carbon atom perpendicular to the plane of the ring. Three valence electrons in the sp 2 hybrid orbitals of each carbon atom and the valence electron of each hydrogen atom form the framework of σ bonds in the benzene molecule. The fourth valence electron of each carbon atom is shared with an adjacent carbon atom in their unhybridized p orbitals to yield the π bonds. Benzene does not, however, exhibit the characteristics typical of an alkene. Each of the six bonds between its carbon atoms is equivalent and exhibits properties that are intermediate between those of a C–C single bond and a double bond. To represent this unique bonding, structural formulas for benzene and its derivatives are typically drawn with single bonds between the carbon atoms and a circle within the ring as shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?