| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
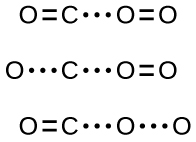
In most circumstances, it is impossible to isolate or identify a transition state or activated complex. In the reaction between carbon monoxide and oxygen to form carbon dioxide, activated complexes have only been observed spectroscopically in systems that utilize a heterogeneous catalyst. The gas-phase reaction occurs too rapidly to isolate any such chemical compound.
Collision theory explains why most reaction rates increase as concentrations increase. With an increase in the concentration of any reacting substance, the chances for collisions between molecules are increased because there are more molecules per unit of volume. More collisions mean a faster reaction rate, assuming the energy of the collisions is adequate.
The minimum energy necessary to form a product during a collision between reactants is called the activation energy ( E a ) . The kinetic energy of reactant molecules plays an important role in a reaction because the energy necessary to form a product is provided by a collision of a reactant molecule with another reactant molecule. (In single-reactant reactions, activation energy may be provided by a collision of the reactant molecule with the wall of the reaction vessel or with molecules of an inert contaminant.) If the activation energy is much larger than the average kinetic energy of the molecules, the reaction will occur slowly: Only a few fast-moving molecules will have enough energy to react. If the activation energy is much smaller than the average kinetic energy of the molecules, the fraction of molecules possessing the necessary kinetic energy will be large; most collisions between molecules will result in reaction, and the reaction will occur rapidly.
[link] shows the energy relationships for the general reaction of a molecule of A with a molecule of B to form molecules of C and D :
The figure shows that the energy of the transition state is higher than that of the reactants A and B by an amount equal to E a , the activation energy. Thus, the sum of the kinetic energies of A and B must be equal to or greater than E a to reach the transition state. After the transition state has been reached, and as C and D begin to form, the system loses energy until its total energy is lower than that of the initial mixture. This lost energy is transferred to other molecules, giving them enough energy to reach the transition state. The forward reaction (that between molecules A and B ) therefore tends to take place readily once the reaction has started. In [link] , Δ H represents the difference in enthalpy between the reactants ( A and B ) and the products ( C and D ). The sum of E a and Δ H represents the activation energy for the reverse reaction:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?