| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If you have ever been in a room when a piping hot pizza was delivered, you have been made aware of the fact that gaseous molecules can quickly spread throughout a room, as evidenced by the pleasant aroma that soon reaches your nose. Although gaseous molecules travel at tremendous speeds (hundreds of meters per second), they collide with other gaseous molecules and travel in many different directions before reaching the desired target. At room temperature, a gaseous molecule will experience billions of collisions per second. The mean free path is the average distance a molecule travels between collisions. The mean free path increases with decreasing pressure; in general, the mean free path for a gaseous molecule will be hundreds of times the diameter of the molecule
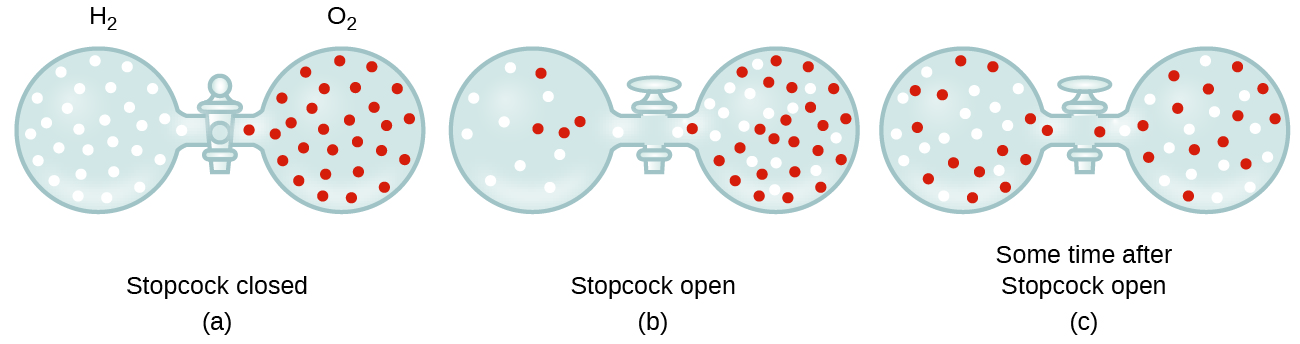
In general, we know that when a sample of gas is introduced to one part of a closed container, its molecules very quickly disperse throughout the container; this process by which molecules disperse in space in response to differences in concentration is called diffusion (shown in [link] ). The gaseous atoms or molecules are, of course, unaware of any concentration gradient, they simply move randomly—regions of higher concentration have more particles than regions of lower concentrations, and so a net movement of species from high to low concentration areas takes place. In a closed environment, diffusion will ultimately result in equal concentrations of gas throughout, as depicted in [link] . The gaseous atoms and molecules continue to move, but since their concentrations are the same in both bulbs, the rates of transfer between the bulbs are equal (no net transfer of molecules occurs).
We are often interested in the rate of diffusion , the amount of gas passing through some area per unit time:
The diffusion rate depends on several factors: the concentration gradient (the increase or decrease in concentration from one point to another); the amount of surface area available for diffusion; and the distance the gas particles must travel. Note also that the time required for diffusion to occur is inversely proportional to the rate of diffusion, as shown in the rate of diffusion equation.
A process involving movement of gaseous species similar to diffusion is effusion , the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole such as a pinhole in a balloon into a vacuum ( [link] ). Although diffusion and effusion rates both depend on the molar mass of the gas involved, their rates are not equal; however, the ratios of their rates are the same.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?