| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We will now extend electrochemistry by determining the relationship between and the thermodynamics quantities such as Δ G ° (Gibbs free energy) and K (the equilibrium constant). In galvanic cells, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy, which can do work. The electrical work is the product of the charge transferred multiplied by the potential difference (voltage):
The charge on 1 mole of electrons is given by Faraday’s constant ( F )
In this equation, n is the number of moles of electrons for the balanced oxidation-reduction reaction. The measured cell potential is the maximum potential the cell can produce and is related to the electrical work ( w ele ) by
The negative sign for the work indicates that the electrical work is done by the system (the galvanic cell) on the surroundings. In an earlier chapter, the free energy was defined as the energy that was available to do work. In particular, the change in free energy was defined in terms of the maximum work ( w max ), which, for electrochemical systems, is w ele .
We can verify the signs are correct when we realize that n and F are positive constants and that galvanic cells, which have positive cell potentials, involve spontaneous reactions. Thus, spontaneous reactions, which have Δ G <0, must have E cell >0. If all the reactants and products are in their standard states, this becomes
This provides a way to relate standard cell potentials to equilibrium constants, since
Most of the time, the electrochemical reactions are run at standard temperature (298.15 K). Collecting terms at this temperature yields
where n is the number of moles of electrons. For historical reasons, the logarithm in equations involving cell potentials is often expressed using base 10 logarithms (log), which changes the constant by a factor of 2.303:
Thus, if Δ G °, K , or is known or can be calculated, the other two quantities can be readily determined. The relationships are shown graphically in [link] .
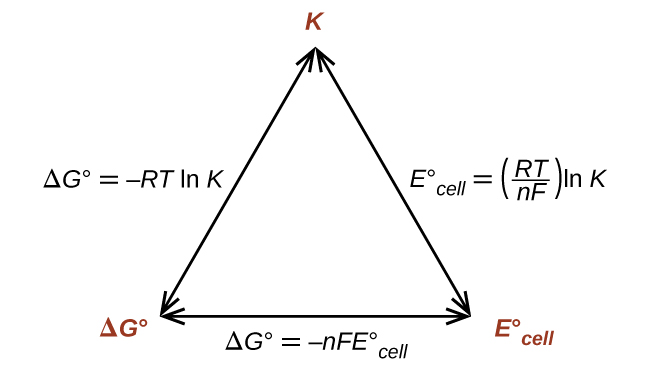
Given any one of the quantities, the other two can be calculated.
Remember that the cell potential for the cathode is not multiplied by two when determining the standard cell potential. With n = 2, the equilibrium constant is then
The two equilibrium constants differ slightly due to rounding in the constants 0.0257 V and 0.0592 V. The standard free energy is then
Check your answer: A positive standard cell potential means a spontaneous reaction, so the standard free energy change should be negative, and an equilibrium constant should be>1.
Spontaneous; n = 2; K = 6.8 10 9 .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?