| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the previous module, the variation of a liquid’s equilibrium vapor pressure with temperature was described. Considering the definition of boiling point, plots of vapor pressure versus temperature represent how the boiling point of the liquid varies with pressure. Also described was the use of heating and cooling curves to determine a substance’s melting (or freezing) point. Making such measurements over a wide range of pressures yields data that may be presented graphically as a phase diagram. A phase diagram combines plots of pressure versus temperature for the liquid-gas, solid-liquid, and solid-gas phase-transition equilibria of a substance. These diagrams indicate the physical states that exist under specific conditions of pressure and temperature, and also provide the pressure dependence of the phase-transition temperatures (melting points, sublimation points, boiling points). A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in [link] .
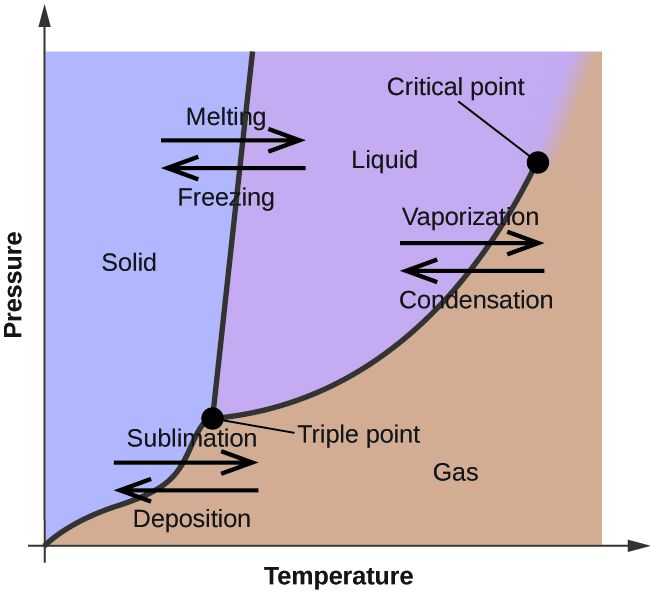
To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in [link] .
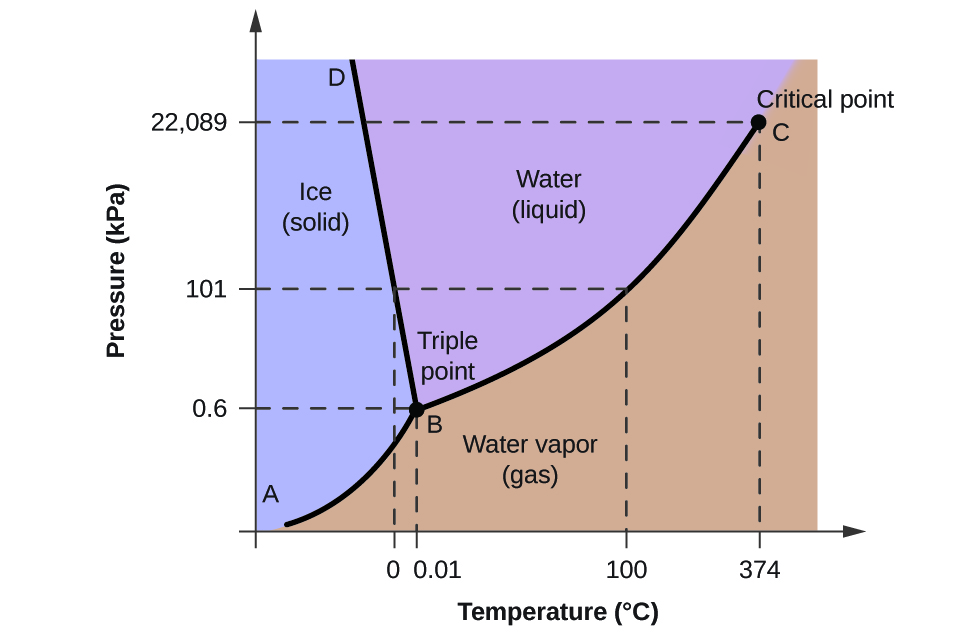
We can use the phase diagram to identify the physical state of a sample of water under specified conditions of pressure and temperature. For example, a pressure of 50 kPa and a temperature of −10 °C correspond to the region of the diagram labeled “ice.” Under these conditions, water exists only as a solid (ice). A pressure of 50 kPa and a temperature of 50 °C correspond to the “water” region—here, water exists only as a liquid. At 25 kPa and 200 °C, water exists only in the gaseous state. Note that on the H 2 O phase diagram, the pressure and temperature axes are not drawn to a constant scale in order to permit the illustration of several important features as described here.
The curve BC in [link] is the plot of vapor pressure versus temperature as described in the previous module of this chapter. This “liquid-vapor” curve separates the liquid and gaseous regions of the phase diagram and provides the boiling point for water at any pressure. For example, at 1 atm, the boiling point is 100 °C. Notice that the liquid-vapor curve terminates at a temperature of 374 °C and a pressure of 218 atm, indicating that water cannot exist as a liquid above this temperature, regardless of the pressure. The physical properties of water under these conditions are intermediate between those of its liquid and gaseous phases. This unique state of matter is called a supercritical fluid, a topic that will be described in the next section of this module.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?