| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
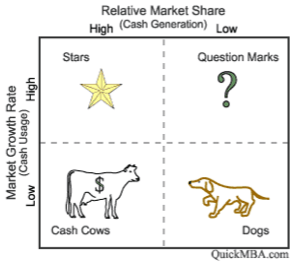
The BCG matrix method is based on the product life cycle theory that can be used to determine what priorities should be given in the product portfolio of a Strategic Business Unit (SBU). To ensure long-term value creation, a company should have a portfolio of products that contains both high-growth products in need of cash inputs and low-growth products that generate a lot of cash. This model can be explained in two dimensions: relative market share and market growth. The basic idea behind this model is that the larger the market share a product has relative to its competitors or the faster the product's market grows, the better it is for the company in an economic sense. The key components of the matrix are illustrated in [link] and discussed below:
Source:
(External Link)
The McKinsey matrix is a later and more advanced form of the BCG Matrix. It has several differences with BCG’s matrix, as discussed below. It is illustrated in Exhibit 6.
Source:
(External Link)
Larry Downes (1999) identifies three new forces that require a totally different perspective towards a strategic framework and a set of very different analytic and business design tools: digitalization, globalization, and deregulation.
Digitalization: As the power of information technology grows, all players in a market will have access to far more information. Thus, totally new business models will emerge in which even players from outside the industry are able to vastly change the basis of competition in a market. Downes gives the example of the rise of electronic shopping malls, operated for instance by telecom operators or credit card organizations. Those who use the Five Forces Model and who base their thinking on today’s industry structure would never see these changes coming in time.
Globalization: Improvements in distribution logistics and communications have allowed nearly all businesses to buy, sell, and cooperate on a global level. Customers, meanwhile, have the chance to shop around and compare prices globally. As a result, even locally oriented mid-sized companies find themselves in a global market, even if they do not export or import themselves. In addition, global and networked markets impose new requirements on organizations' strategies. It is not enough any more to position oneself as a price-leader or quality-leader (as Porter suggests in his Generic Strategies model). Rather, competitive advantages emerge now from the ability to develop lasting relationships to more mobile custumers and to manage far-reaching networks of partners for mutual advantage.
Deregulation: The past decade has seen a dramatic shrinking of government influence in many industries like airlines, communications, utilities, and banking in the US and in Europe. Fueled by the new opportunities provided by information technology, organizations in these industries were able and forced to completely restructure their businesses and to be on the lookout for new opportunities and competitive threats. For example, traditional land line telephone companies that did not enter the wireless telephony market found themselves with a shrinking customer base. This is because young people frequently use only cell phones now and do not bother to have a land line phone in their homes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?