| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are many benefits that technology can bring to an operations environment. Automated machinery, programmable equipment, and management information systems can provide speed, low unit processing costs, labor cost savings, increased accuracy and consistency, and sophisticated tracking and decision support systems to increase operations efficiency and effectiveness for both manufacturing and service environments. The main drawback in many technology decisions is the high fixed cost of purchasing and implementing the new systems. If mistakes are made in technology purchases, it can severely impact the fortunes of the company.
Managers are often biased in favor of adopting leading edge technology, especially if they see their competitors adopting it. Financial justifications for purchasing new technology are often overly optimistic in estimations of payback periods, the costs of implementation, and the actual gains in overall productivity the firm will enjoy.
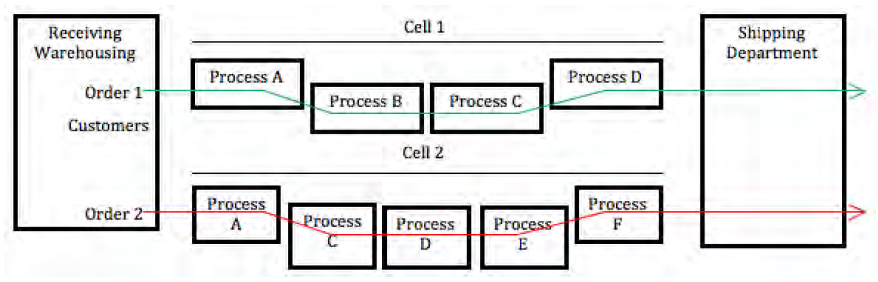
The challenge for managers in technology is selecting the right technology for the right application. For example, if a manufacturing company believes that automation will increase the firm’s flexibility to adapt to a changing competitive environment, questions should be asked, such as:
Deere&Co manufactures machinery for the highly cyclical agricultural and construction industries. One of the reasons for Deere’s success over the many decades is its ability to keep its technology expenditures under control so it can weather the inevitable declines in demand for its products. Deere managers use a mix of low technology/labor intensive production methods and automated/programmable technologies in its manufacturing plants. Careful technology decision making is a major reason why Deere&Co continues to thrive in spite of its highly volatile markets.
There are many factors that can determine where an organization will locate its facilities. For any given situation, some factors become more important than others in how facility location affects an organization’s efficiency and effectiveness.
In the 1990s, MCI, a major US telecommunications company, decided to relocate its engineering services division from MCI’s headquarters in Washington DC to Colorado Springs, Colorado to reduce labor and facility costs. The decision was largely unsuccessful due to the high costs of employee relocation and the fact that much of the ethnically diverse engineering workforce did not want to live in Colorado Springs. Unlike Washington DC, Colorado Springs did not have cultural diversity to match with its diverse and highly educated workforce, it lacked employment options for spouses, and the work ethic was more relaxed due to the beautiful natural setting that provided unlimited options for outdoor recreation. In short, if MCI had put more effort into researching how well the Colorado Springs location matched its strategic requirements, it probably could have saved itself millions of dollars and a great deal of internal disruption to the organization.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?