| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As the business grows, its organizational structure is heavily influenced by function (people grouped with similar responsibilities), process (people involved in similar processes), product (people building a specific product) or projects (members of a project). “Entrepreneurial Firms: An Examination of Organizational Structure and Management Roles Across Life Cycle Stages,” Watson, Kathleen M., Plascha, Gerhard R., paper presented at U.S. Association for Small Business and Entrepreneurship annual conference, Baltimore, Maryland, October 1993) A firm's structure might be influenced by some or all of these types of departmentation. Large firms usually employ a variety of departmentation styles, selecting the most appropriate form for each subsystem.
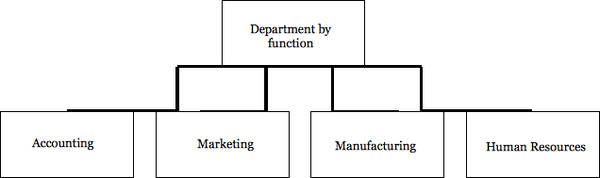
Grouping activities by function is the most widely used form of departmentation. Similar activities are housed in a department or under a single chain of command. For example, sales, advertising, public relations, and promotion might be grouped in a marketing department; employee benefits, employee training and employee regulatory compliance may be housed in the human relations department and so on.
Functional departmentation takes advantage of employees’ specialization. Employees with similar training, education, skills, or equipment work together and under a supervisor responsible for that department's activities. Because one supervisor typically oversees a major area of activity, functional departmentation also facilitates coordination. For instance in a larger retail operation, one marketing department supervisor would control and coordinate the work of buyers, merchandisers and the sales force so that information and activities of each function would be more efficient and productive.
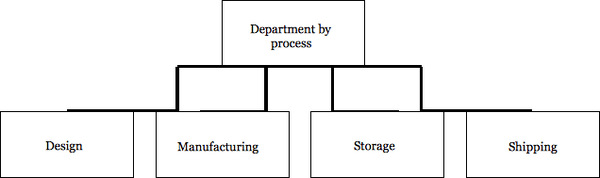
The process or equipment used in producing a product or service may be the basis for determining departmental units. Since a certain amount of expertise or training is required to handle complicated processes or complex machinery, activities that involve the use of specialized equipment may be grouped into a separate department.
This form of departmentation is similar to functional departmentation. The grouping of all milling machines into one department or the placing of lathes in another department is illustrative of departmentation by equipment or process. As a further example, a large food products firm may be departmentalized by processes such as manufacturing, package design, distribution, and shipping.3
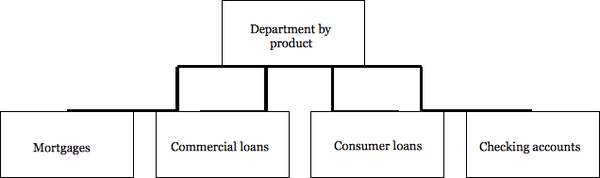
Companies with diversified product lines frequently create departmental units based on the product. To departmentalize on a product basis means to establish each major product in a product line as an independent unit within the overall structure of the company. For instance, retail stores may organize their operations to meet the needs of specific customer groups by forming special departments to cater to house wares, menswear, children’s clothing and so forth. Product departmentation can be a useful guide for grouping activities in service businesses as well. Many banks have separate departments for mortgages, checking accounts and commercial loans.
Project organizations are specifically designed to deal with changing environments. A project in this sense is a series of related activities required to accomplish a work outcome, such as the development of a new product. Projects and task forces or teams are generally unique—designed to work on a nonrecurring project. They are tightly organized units under the direction of a manager with broad powers of authority.
A team is given a project with specific tasks or operational concerns. This team is composed of employees from the firm who have expertise or skills that can be applied directly to the project. The members of the team manage the project without direct supervision and assume responsibility for the results. When work teams function well, the need for a large number of supervisors decreases.
Some firms are organized by using a mix of departmentation types (matrix organization). It is not unusual to see firms that utilize the function and project organization combination. The same is true for process and project as well as other combinations. For instance, a large hospital could have an accounting department, surgery department, marketing department, and a satellite center project team that make up its organizational structure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?