| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is so named because the ribosomes attached to its cytoplasmic surface give it a studded appearance when viewed through an electron microscope.
The ribosomes synthesize proteins while attached to the ER, resulting in transfer of their newly synthesized proteins into the lumen of the RER where they undergo modifications such as folding or addition of sugars. The RER also makes phospholipids for cell membranes.
If the phospholipids or modified proteins are not destined to stay in the RER, they will be packaged within vesicles and transported from the RER by budding from the membrane ( [link] ). Since the RER is engaged in modifying proteins that will be secreted from the cell, it is abundant in cells that secrete proteins, such as the liver.
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is continuous with the RER but has few or no ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface (see [link] ). The SER’s functions include synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids (including phospholipids), and steroid hormones; detoxification of medications and poisons; alcohol metabolism; and storage of calcium ions.
We have already mentioned that vesicles can bud from the ER, but where do the vesicles go? Before reaching their final destination, the lipids or proteins within the transport vesicles need to be sorted, packaged, and tagged so that they wind up in the right place. The sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins take place in the Golgi apparatus (also called the Golgi body), a series of flattened membranous sacs ( [link] ).
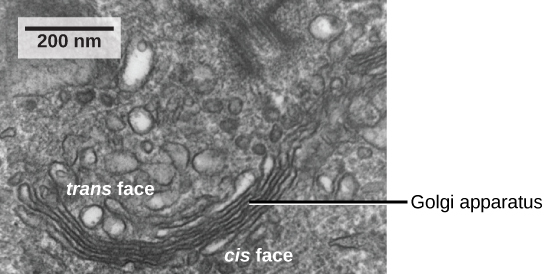
The Golgi apparatus has a receiving face near the endoplasmic reticulum and a releasing face on the side away from the ER, toward the cell membrane. The transport vesicles that form from the ER travel to the receiving face, fuse with it, and empty their contents into the lumen of the Golgi apparatus. As the proteins and lipids travel through the Golgi, they undergo further modifications. The most frequent modification is the addition of short chains of sugar molecules. The newly modified proteins and lipids are then tagged with small molecular groups to enable them to be routed to their proper destinations.
Finally, the modified and tagged proteins are packaged into vesicles that bud from the opposite face of the Golgi. While some of these vesicles, transport vesicles, deposit their contents into other parts of the cell where they will be used, others, secretory vesicles, fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents outside the cell.
The amount of Golgi in different cell types again illustrates that form follows function within cells. Cells that engage in a great deal of secretory activity (such as cells of the salivary glands that secrete digestive enzymes or cells of the immune system that secrete antibodies) have an abundant number of Golgi.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?