| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
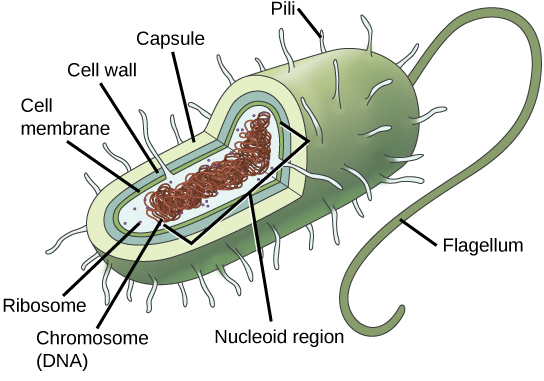
Both Bacteria and Archaea are types of prokaryotic cells. They differ in the lipid composition of their cell membranes and in the characteristics of their cell walls. Both types of prokaryotes have the same basic structures, but these are built from different chemical components that are evidence of an ancient separation of their lineages. The archaeal plasma membrane is chemically different from the bacterial membrane; some archaeal membranes are lipid monolayers instead of phosopholipid bilayers.
The cell wall is a protective layer that surrounds some prokaryotic cells and gives them shape and rigidity. It is located outside the cell membrane and prevents osmotic lysis (bursting caused by increasing volume). The chemical compositions of the cell walls vary between Archaea and Bacteria, as well as between bacterial species. Bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan , composed of polysaccharide chains cross-linked to peptides. Bacteria are divided into two major groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative , based on their reaction to a procedure called Gram staining. The different bacterial responses to the staining procedure are caused by cell wall structure. Gram-positive organisms have a thick wall consisting of many layers of peptidoglycan. Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner cell wall composed of a few layers of peptidoglycan and additional structures, surrounded by an outer membrane ( [link] ).
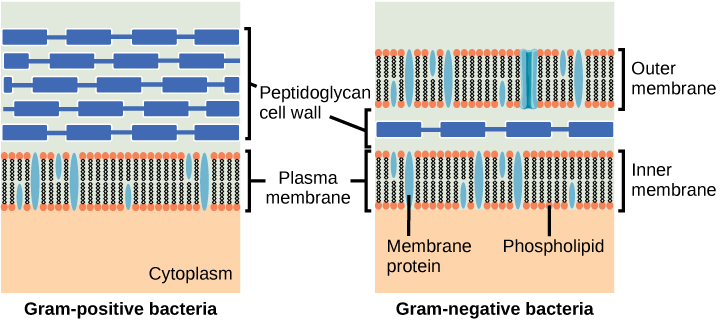
Which of the following statements is true?
Archaeal cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan. There are four different types of archaeal cell walls. One type is composed of pseudopeptidoglycan . The other three types of cell walls contain polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and surface-layer proteins known as S-layers.
Reproduction in prokaryotes is primarily asexual and takes place by binary fission. Recall that the DNA of a prokaryote exists usually as a single, circular chromosome. Prokaryotes do not undergo mitosis. Rather, the chromosome loop is replicated, and the two resulting copies attached to the plasma membrane move apart as the cell grows in a process called binary fission. The prokaryote, now enlarged, is pinched inward at its equator, and the two resulting cells, which are clones, separate. Binary fission does not provide an opportunity for genetic recombination, but prokaryotes can alter their genetic makeup in three ways.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?