| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Not all cells adhere to the classic cell-cycle pattern in which a newly formed daughter cell immediately enters interphase, closely followed by the mitotic phase. Cells in the G 0 phase are not actively preparing to divide. The cell is in a quiescent (inactive) stage, having exited the cell cycle. Some cells enter G 0 temporarily until an external signal triggers the onset of G 1 . Other cells that never or rarely divide, such as mature cardiac muscle and nerve cells, remain in G 0 permanently ( [link] ).
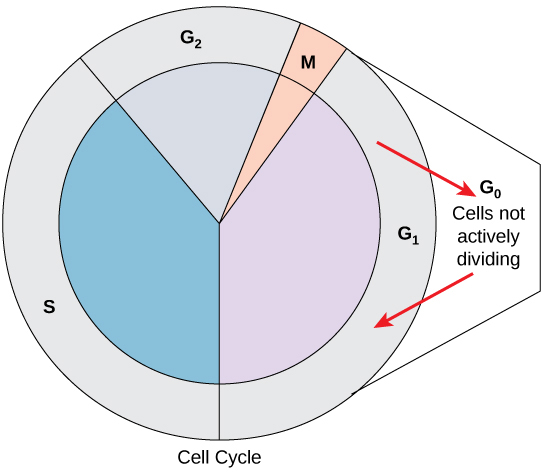
The length of the cell cycle is highly variable even within the cells of an individual organism. In humans, the frequency of cell turnover ranges from a few hours in early embryonic development to an average of two to five days for epithelial cells, or to an entire human lifetime spent in G 0 by specialized cells such as cortical neurons or cardiac muscle cells. There is also variation in the time that a cell spends in each phase of the cell cycle. When fast-dividing mammalian cells are grown in culture (outside the body under optimal growing conditions), the length of the cycle is approximately 24 hours. In rapidly dividing human cells with a 24-hour cell cycle, the G 1 phase lasts approximately 11 hours. The timing of events in the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell.
It is essential that daughter cells be exact duplicates of the parent cell. Mistakes in the duplication or distribution of the chromosomes lead to mutations that may be passed forward to every new cell produced from the abnormal cell. To prevent a compromised cell from continuing to divide, there are internal control mechanisms that operate at three main cell cycle checkpoints at which the cell cycle can be stopped until conditions are favorable. These checkpoints occur near the end of G 1 , at the G 2 –M transition, and during metaphase ( [link] ).
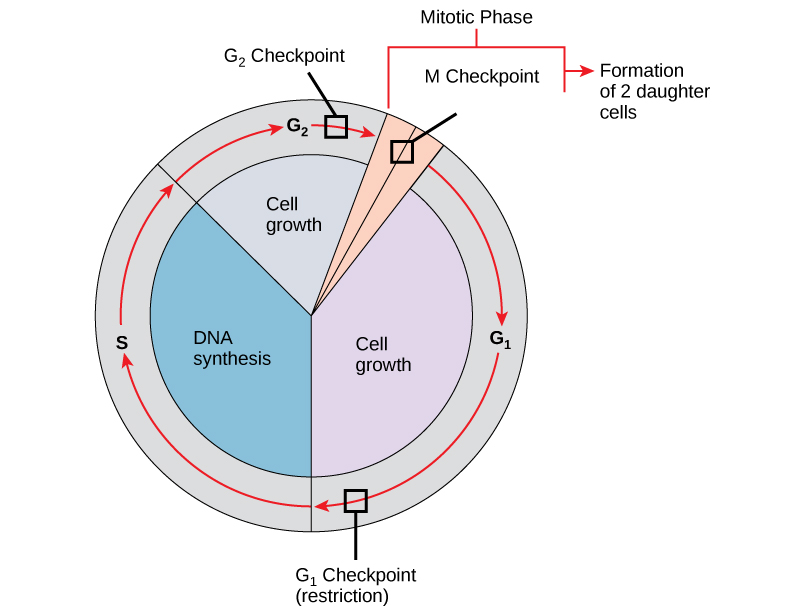
The G 1 checkpoint determines whether all conditions are favorable for cell division to proceed. The G 1 checkpoint, also called the restriction point, is the point at which the cell irreversibly commits to the cell-division process. In addition to adequate reserves and cell size, there is a check for damage to the genomic DNA at the G 1 checkpoint. A cell that does not meet all the requirements will not be released into the S phase.
The G 2 checkpoint bars the entry to the mitotic phase if certain conditions are not met. As in the G 1 checkpoint, cell size and protein reserves are assessed. However, the most important role of the G 2 checkpoint is to ensure that all of the chromosomes have been replicated and that the replicated DNA is not damaged.
The M checkpoint occurs near the end of the metaphase stage of mitosis. The M checkpoint is also known as the spindle checkpoint because it determines if all the sister chromatids are correctly attached to the spindle microtubules. Because the separation of the sister chromatids during anaphase is an irreversible step, the cycle will not proceed until the kinetochores of each pair of sister chromatids are firmly anchored to spindle fibers arising from opposite poles of the cell.
Watch what occurs at the G 1 , G 2 , and M checkpoints by visiting this animation of the cell cycle.
The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Interphase is divided into G 1 , S, and G 2 phases. Mitosis consists of five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis is usually accompanied by cytokinesis, during which the cytoplasmic components of the daughter cells are separated either by an actin ring (animal cells) or by cell plate formation (plant cells).
Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: one near the end of G 1 , a second at the G 2 –M transition, and the third during metaphase.
[link] Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis?
[link] D. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks apart and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?