| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Hormone production and release are primarily controlled by negative feedback, as described in the discussion on homeostasis. In this way, the concentration of hormones in blood is maintained within a narrow range. For example, the anterior pituitary signals the thyroid to release thyroid hormones. Increasing levels of these hormones in the blood then give feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to inhibit further signaling to the thyroid gland ( [link] ).
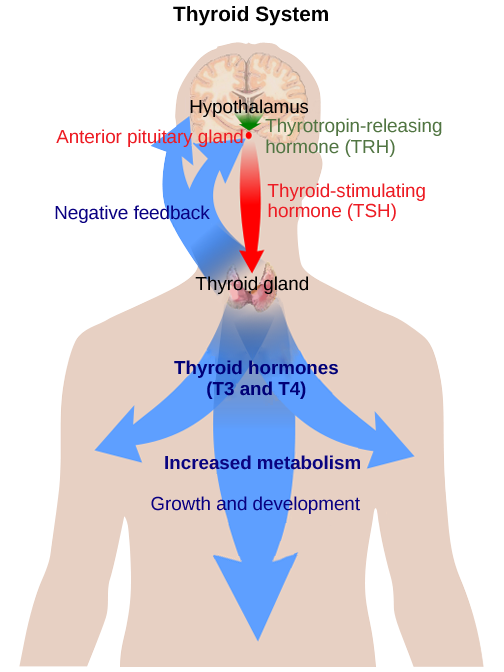
Goiter, a disease caused by iodine deficiency, results in the inability of the thyroid gland to form T 3 and T 4 . The body typically attempts to compensate by producing greater amounts of TSH. Which of the following symptoms would you expect goiter to cause?
Hormones cause cellular changes by binding to receptors on or in target cells. The number of receptors on a target cell can increase or decrease in response to hormone activity.
Hormone levels are primarily controlled through negative feedback, in which rising levels of a hormone inhibit its further release.
The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain. The anterior pituitary receives signals from the hypothalamus and produces six hormones. The posterior pituitary is an extension of the brain and releases hormones (antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin) produced by the hypothalamus. The thyroid gland is located in the neck and is composed of two lobes. The thyroid produces the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin. The parathyroid glands lie on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland and produce parathyroid hormone.
The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys and consist of the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. The adrenal cortex produces the corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. The adrenal medulla is the inner part of the adrenal gland and produces epinephrine and norepinephrine.
The pancreas lies in the abdomen between the stomach and the small intestine. Clusters of endocrine cells in the pancreas form the islets of Langerhans, which contain alpha cells that release glucagon and beta cells that release insulin. Some organs possess endocrine activity as a secondary function but have another primary function. The heart produces the hormone atrial natriuretic peptide, which functions to reduce blood volume, pressure, and Na + concentration. The gastrointestinal tract produces various hormones that aid in digestion. The kidneys produce erythropoietin. The thymus produces hormones that aid in the development of the immune system. The gonads produce steroid hormones, including testosterone in males and estrogen and progesterone in females. Adipose tissue produces leptin, which promotes satiety signals in the brain.
[link] Goiter, a disease caused by iodine deficiency, results in the inability of the thyroid gland to form T 3 and T 4 . The body typically attempts to compensate by producing greater amounts of TSH. Which of the following symptoms would you expect goiter to cause?
[link] A

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?