| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Living things are highly organized and structured, following a hierarchy on a scale from small to large. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atoms form molecules. A molecule is a chemical structure consisting of at least two atoms held together by a chemical bond. Many molecules that are biologically important are macromolecules , large molecules that are typically formed by combining smaller units called monomers. An example of a macromolecule is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ( [link] ), which contains the instructions for the functioning of the organism that contains it.
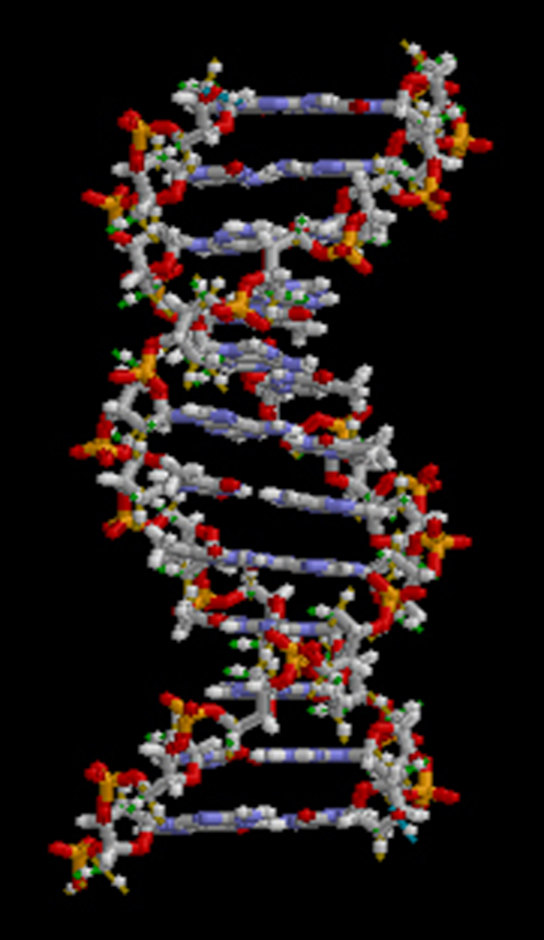
To see an animation of this DNA molecule, click here .
Some cells contain aggregates of macromolecules surrounded by membranes; these are called organelles . Organelles are small structures that exist within cells and perform specialized functions. All living things are made of cells; the cell itself is the smallest fundamental unit of structure and function in living organisms. (This requirement is why viruses are not considered living: they are not made of cells. To make new viruses, they have to invade and hijack a living cell; only then can they obtain the materials they need to reproduce.) Some organisms consist of a single cell and others are multicellular. Cells are classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that lack organelles surrounded by a membrane and do not have nuclei surrounded by nuclear membranes; in contrast, the cells of eukaryotes do have membrane-bound organelles and nuclei.
In most multicellular organisms, cells combine to make tissues , which are groups of similar cells carrying out the same function. Organs are collections of tissues grouped together based on a common function. Organs are present not only in animals but also in plants. An organ system is a higher level of organization that consists of functionally related organs. For example vertebrate animals have many organ systems, such as the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body and to and from the lungs; it includes organs such as the heart and blood vessels. Organisms are individual living entities. For example, each tree in a forest is an organism. Single-celled prokaryotes and single-celled eukaryotes are also considered organisms and are typically referred to as microorganisms.
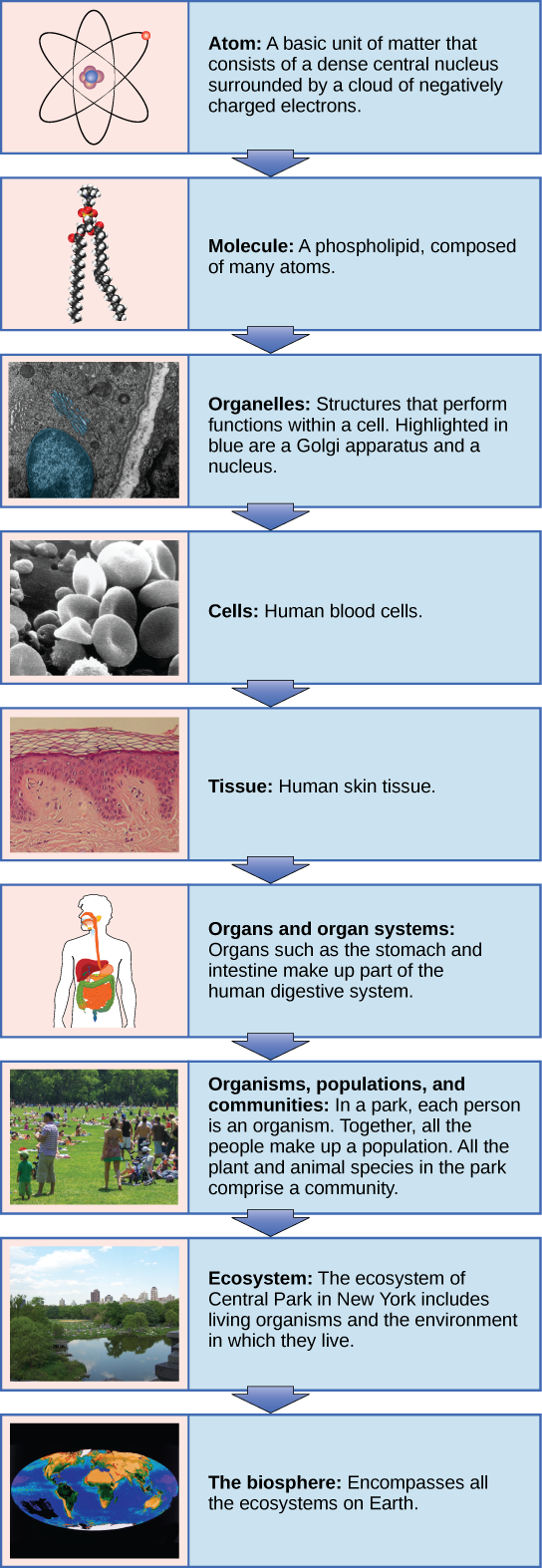
Which of the following statements is false?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?