| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
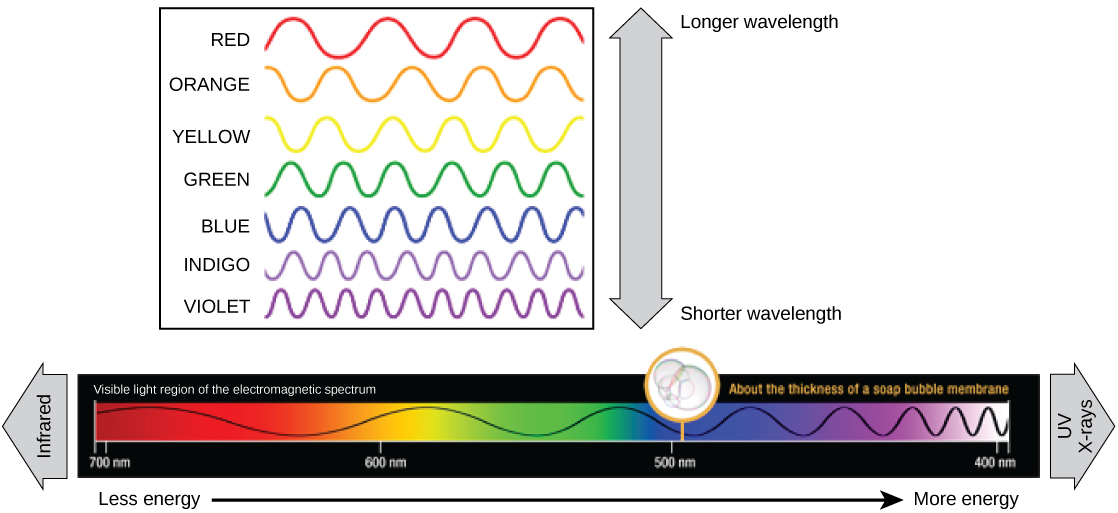
The visible light seen by humans as white light actually exists in a rainbow of colors. Certain objects, such as a prism or a drop of water, disperse white light to reveal the colors to the human eye. The visible light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum shows the rainbow of colors, with violet and blue having shorter wavelengths, and therefore higher energy. At the other end of the spectrum toward red, the wavelengths are longer and have lower energy ( [link] ).
Different kinds of pigments exist, and each has evolved to absorb only certain wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect or transmit the wavelengths they cannot absorb, making them appear in the corresponding color.
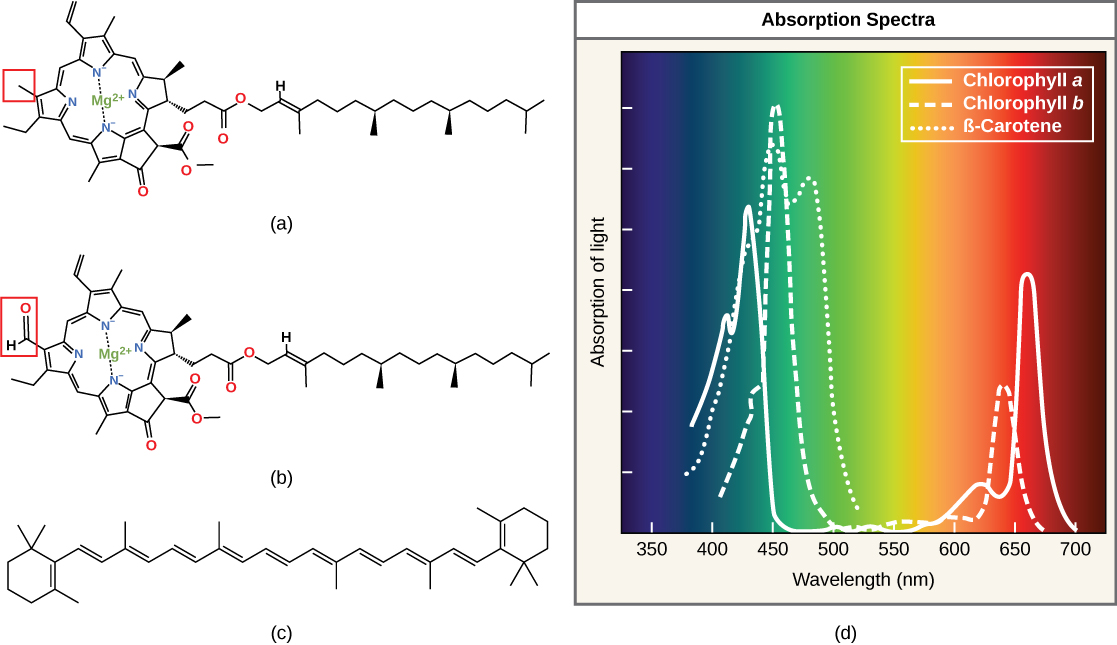
Chlorophylls and carotenoids are the two major classes of photosynthetic pigments found in plants and algae; each class has multiple types of pigment molecules. There are five major chlorophylls: a , b , c and d and a related molecule found in prokaryotes called bacteriochlorophyll. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are found in higher plant chloroplasts and will be the focus of the following discussion.
With dozens of different forms, carotenoids are a much larger group of pigments. The carotenoids found in fruit—such as the red of tomato (lycopene), the yellow of corn seeds (zeaxanthin), or the orange of an orange peel (β-carotene)—are used as advertisements to attract seed dispersers. In photosynthesis, carotenoids function as photosynthetic pigments that are very efficient molecules for the disposal of excess energy. When a leaf is exposed to full sun, the light-dependent reactions are required to process an enormous amount of energy; if that energy is not handled properly, it can do significant damage. Therefore, many carotenoids reside in the thylakoid membrane, absorb excess energy, and safely dissipate that energy as heat.
Each type of pigment can be identified by the specific pattern of wavelengths it absorbs from visible light, which is the absorption spectrum . The graph in [link] shows the absorption spectra for chlorophyll a , chlorophyll b , and a type of carotenoid pigment called β-carotene (which absorbs blue and green light). Notice how each pigment has a distinct set of peaks and troughs, revealing a highly specific pattern of absorption. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not green. Because green is reflected or transmitted, chlorophyll appears green. Carotenoids absorb in the short-wavelength blue region, and reflect the longer yellow, red, and orange wavelengths.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?