| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Internal female reproductive structures include ovaries, oviducts, the uterus , and the vagina, shown in [link] . The pair of ovaries is held in place in the abdominal cavity by a system of ligaments. Ovaries consist of a medulla and cortex: the medulla contains nerves and blood vessels to supply the cortex with nutrients and remove waste. The outer layers of cells of the cortex are the functional parts of the ovaries. The cortex is made up of follicular cells that surround eggs that develop during fetal development in utero . During the menstrual period, a batch of follicular cells develops and prepares the eggs for release. At ovulation, one follicle ruptures and one egg is released, as illustrated in [link] a .
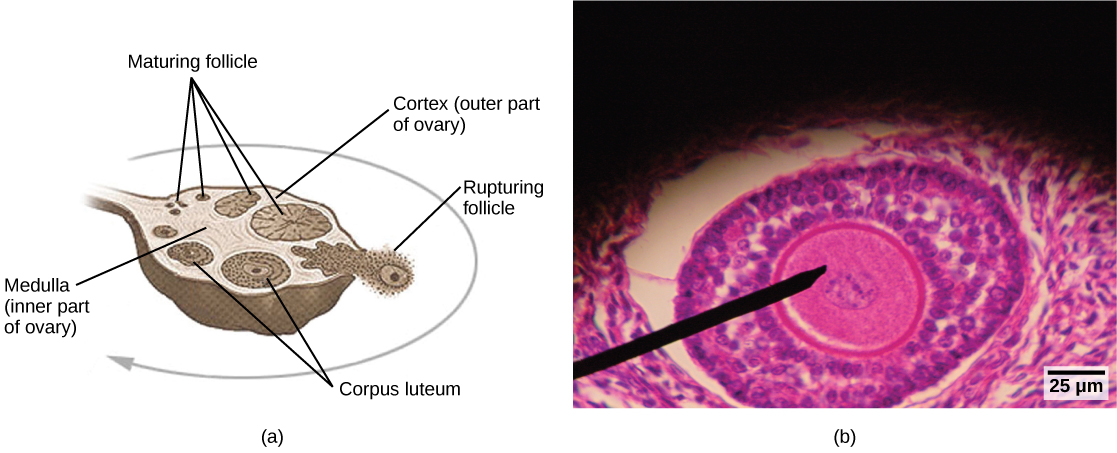
The oviducts , or fallopian tubes, extend from the uterus in the lower abdominal cavity to the ovaries, but they are not in contact with the ovaries. The lateral ends of the oviducts flare out into a trumpet-like structure and have a fringe of finger-like projections called fimbriae, illustrated in [link] b . When an egg is released at ovulation, the fimbrae help the non-motile egg enter into the tube and passage to the uterus. The walls of the oviducts are ciliated and are made up mostly of smooth muscle. The cilia beat toward the middle, and the smooth muscle contracts in the same direction, moving the egg toward the uterus. Fertilization usually takes place within the oviducts and the developing embryo is moved toward the uterus for development. It usually takes the egg or embryo a week to travel through the oviduct. Sterilization in women is called a tubal ligation; it is analogous to a vasectomy in males in that the oviducts are severed and sealed.
The uterus is a structure about the size of a woman’s fist. This is lined with an endometrium rich in blood vessels and mucus glands. The uterus supports the developing embryo and fetus during gestation. The thickest portion of the wall of the uterus is made of smooth muscle. Contractions of the smooth muscle in the uterus aid in passing the baby through the vagina during labor. A portion of the lining of the uterus sloughs off during each menstrual period, and then builds up again in preparation for an implantation. Part of the uterus, called the cervix, protrudes into the top of the vagina. The cervix functions as the birth canal.
The vagina is a muscular tube that serves several purposes. It allows menstrual flow to leave the body. It is the receptacle for the penis during intercourse and the vessel for the delivery of offspring. It is lined by stratified squamous epithelial cells to protect the underlying tissue.
The sexual response in humans is both psychological and physiological. Both sexes experience sexual arousal through psychological and physical stimulation. There are four phases of the sexual response. During phase one, called excitement, vasodilation leads to vasocongestion in erectile tissues in both men and women. The nipples, clitoris, labia, and penis engorge with blood and become enlarged. Vaginal secretions are released to lubricate the vagina to facilitate intercourse. During the second phase, called the plateau, stimulation continues, the outer third of the vaginal wall enlarges with blood, and breathing and heart rate increase.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?