| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
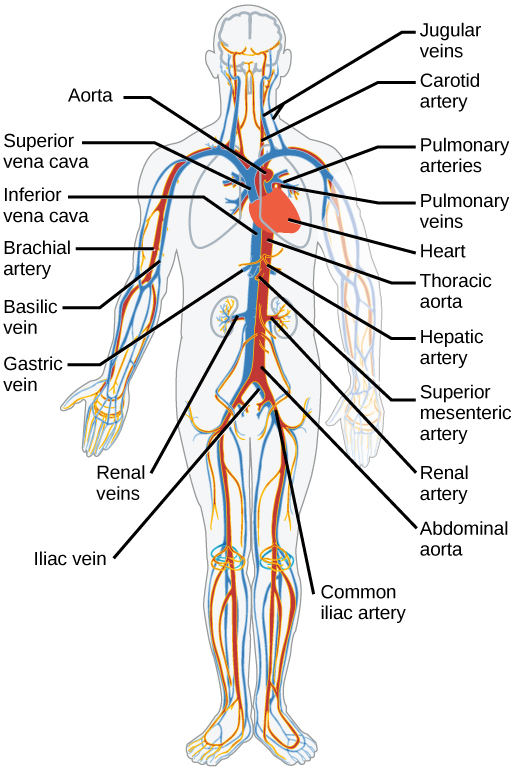
Arterioles diverge into capillary beds. Capillary beds contain a large number (10 to 100) of capillaries that branch among the cells and tissues of the body. Capillaries are narrow-diameter tubes that can fit red blood cells through in single file and are the sites for the exchange of nutrients, waste, and oxygen with tissues at the cellular level. Fluid also crosses into the interstitial space from the capillaries. The capillaries converge again into venules that connect to minor veins that finally connect to major veins that take blood high in carbon dioxide back to the heart. Veins are blood vessels that bring blood back to the heart. The major veins drain blood from the same organs and limbs that the major arteries supply. Fluid is also brought back to the heart via the lymphatic system.
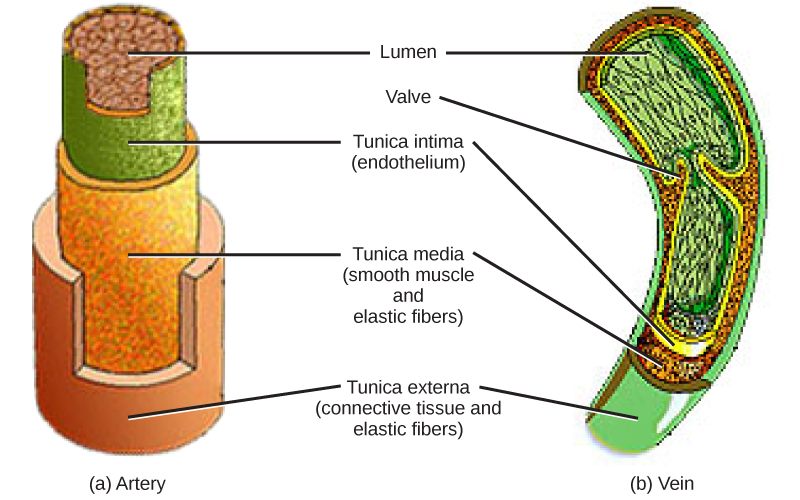
The structure of the different types of blood vessels reflects their function or layers. There are three distinct layers, or tunics, that form the walls of blood vessels ( [link] ). The first tunic is a smooth, inner lining of endothelial cells that are in contact with the red blood cells. The endothelial tunic is continuous with the endocardium of the heart. In capillaries, this single layer of cells is the location of diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the endothelial cells and red blood cells, as well as the exchange site via endocytosis and exocytosis. The movement of materials at the site of capillaries is regulated by vasoconstriction , narrowing of the blood vessels, and vasodilation , widening of the blood vessels; this is important in the overall regulation of blood pressure.
Veins and arteries both have two further tunics that surround the endothelium: the middle tunic is composed of smooth muscle and the outermost layer is connective tissue (collagen and elastic fibers). The elastic connective tissue stretches and supports the blood vessels, and the smooth muscle layer helps regulate blood flow by altering vascular resistance through vasoconstriction and vasodilation. The arteries have thicker smooth muscle and connective tissue than the veins to accommodate the higher pressure and speed of freshly pumped blood. The veins are thinner walled as the pressure and rate of flow are much lower. In addition, veins are structurally different than arteries in that veins have valves to prevent the backflow of blood. Because veins have to work against gravity to get blood back to the heart, contraction of skeletal muscle assists with the flow of blood back to the heart.
The heart muscle pumps blood through three divisions of the circulatory system: coronary, pulmonary, and systemic. There is one atrium and one ventricle on the right side and one atrium and one ventricle on the left side. The pumping of the heart is a function of cardiomyocytes, distinctive muscle cells that are striated like skeletal muscle but pump rhythmically and involuntarily like smooth muscle. The internal pacemaker starts at the sinoatrial node, which is located near the wall of the right atrium. Electrical charges pulse from the SA node causing the two atria to contract in unison; then the pulse reaches the atrioventricular node between the right atrium and right ventricle. A pause in the electric signal allows the atria to empty completely into the ventricles before the ventricles pump out the blood. The blood from the heart is carried through the body by a complex network of blood vessels; arteries take blood away from the heart, and veins bring blood back to the heart.
[link] Which of the following statements about the circulatory system is false?
[link] C
[link] Which of the following statements about the heart is false?
[link] B

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?