| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
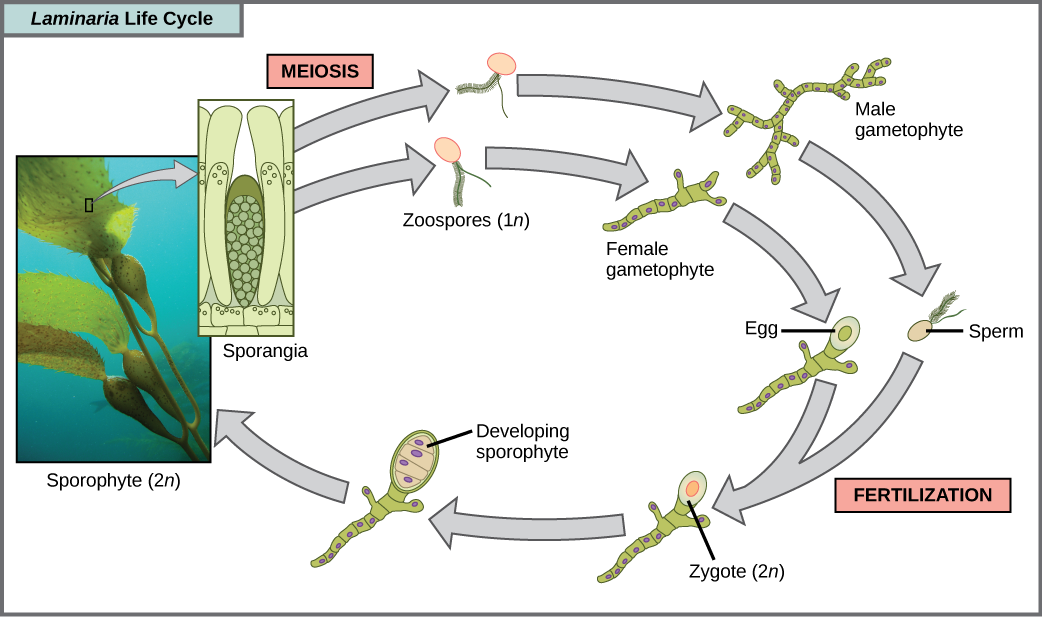
Which of the following statements about the Laminaria life cycle is false?
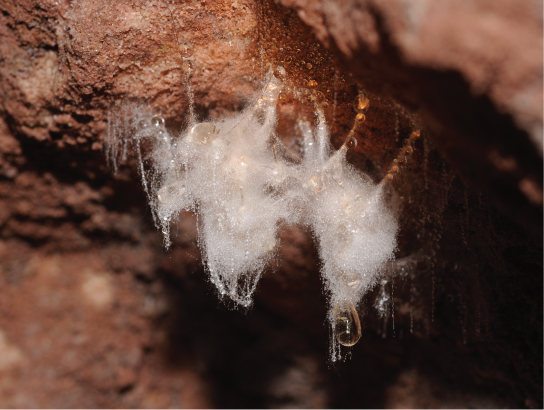
The water molds, oomycetes (“egg fungus”), were so-named based on their fungus-like morphology, but molecular data have shown that the water molds are not closely related to fungi. The oomycetes are characterized by a cellulose-based cell wall and an extensive network of filaments that allow for nutrient uptake. As diploid spores, many oomycetes have two oppositely directed flagella (one hairy and one smooth) for locomotion. The oomycetes are nonphotosynthetic and include many saprobes and parasites. The saprobes appear as white fluffy growths on dead organisms ( [link] ). Most oomycetes are aquatic, but some parasitize terrestrial plants. One plant pathogen is Phytophthora infestans , the causative agent of late blight of potatoes, such as occurred in the nineteenth century Irish potato famine.

The Rhizaria supergroup includes many of the amoebas, most of which have threadlike or needle-like pseudopodia ( [link] ). Pseudopodia function to trap and engulf food particles and to direct movement in rhizarian protists. These pseudopods project outward from anywhere on the cell surface and can anchor to a substrate. The protist then transports its cytoplasm into the pseudopod, thereby moving the entire cell. This type of motion, called cytoplasmic streaming , is used by several diverse groups of protists as a means of locomotion or as a method to distribute nutrients and oxygen.
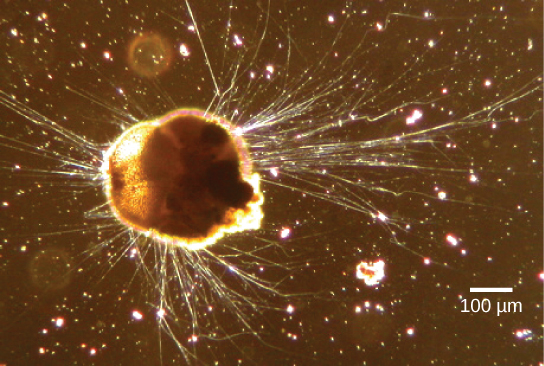
Take a look at this video to see cytoplasmic streaming in a green alga.
Foraminiferans, or forams, are unicellular heterotrophic protists, ranging from approximately 20 micrometers to several centimeters in length, and occasionally resembling tiny snails ( [link] ). As a group, the forams exhibit porous shells, called tests that are built from various organic materials and typically hardened with calcium carbonate. The tests may house photosynthetic algae, which the forams can harvest for nutrition. Foram pseudopodia extend through the pores and allow the forams to move, feed, and gather additional building materials. Typically, forams are associated with sand or other particles in marine or freshwater habitats. Foraminiferans are also useful as indicators of pollution and changes in global weather patterns.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?