| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
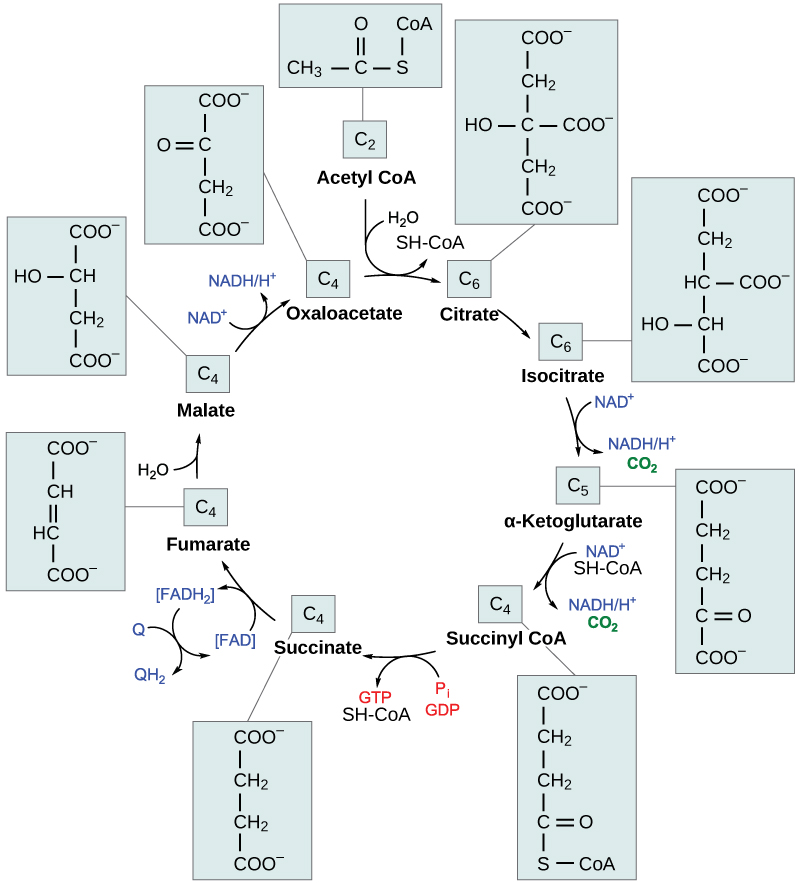
Step 1. Prior to the start of the first step, a transitional phase occurs during which pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl CoA. Then, the first step of the cycle begins: This is a condensation step, combining the two-carbon acetyl group with a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon molecule of citrate. CoA is bound to a sulfhydryl group (-SH) and diffuses away to eventually combine with another acetyl group. This step is irreversible because it is highly exergonic. The rate of this reaction is controlled by negative feedback and the amount of ATP available. If ATP levels increase, the rate of this reaction decreases. If ATP is in short supply, the rate increases.
Step 2. In step two, citrate loses one water molecule and gains another as citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate.
Step 3. In step three, isocitrate is oxidized, producing a five-carbon molecule, α-ketoglutarate, together with a molecule of CO 2 and two electrons, which reduce NAD + to NADH. This step is also regulated by negative feedback from ATP and NADH, and a positive effect of ADP.
Steps 3 and 4. Steps three and four are both oxidation and decarboxylation steps, which release electrons that reduce NAD + to NADH and release carboxyl groups that form CO 2 molecules. α-Ketoglutarate is the product of step three, and a succinyl group is the product of step four. CoA binds the succinyl group to form succinyl CoA. The enzyme that catalyzes step four is regulated by feedback inhibition of ATP, succinyl CoA, and NADH.
Step 5. In step five, a phosphate group is substituted for coenzyme A, and a high-energy bond is formed. This energy is used in substrate-level phosphorylation (during the conversion of the succinyl group to succinate) to form either guanine triphosphate (GTP) or ATP. There are two forms of the enzyme, called isoenzymes, for this step, depending upon the type of animal tissue in which they are found. One form is found in tissues that use large amounts of ATP, such as heart and skeletal muscle. This form produces ATP. The second form of the enzyme is found in tissues that have a high number of anabolic pathways, such as liver. This form produces GTP. GTP is energetically equivalent to ATP; however, its use is more restricted. In particular, protein synthesis primarily uses GTP.
Step 6. Step six is a dehydration process that converts succinate into fumarate. Two hydrogen atoms are transferred to FAD, producing FADH 2 . The energy contained in the electrons of these atoms is insufficient to reduce NAD + but adequate to reduce FAD. Unlike NADH, this carrier remains attached to the enzyme and transfers the electrons to the electron transport chain directly. This process is made possible by the localization of the enzyme catalyzing this step inside the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Step 7. Water is added to fumarate during step seven, and malate is produced. The last step in the citric acid cycle regenerates oxaloacetate by oxidizing malate. Another molecule of NADH is produced in the process.
Click through each step of the citric acid cycle here .
Two carbon atoms come into the citric acid cycle from each acetyl group, representing four out of the six carbons of one glucose molecule. Two carbon dioxide molecules are released on each turn of the cycle; however, these do not necessarily contain the most recently added carbon atoms. The two acetyl carbon atoms will eventually be released on later turns of the cycle; thus, all six carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule are eventually incorporated into carbon dioxide. Each turn of the cycle forms three NADH molecules and one FADH 2 molecule. These carriers will connect with the last portion of aerobic respiration to produce ATP molecules. One GTP or ATP is also made in each cycle. Several of the intermediate compounds in the citric acid cycle can be used in synthesizing non-essential amino acids; therefore, the cycle is amphibolic (both catabolic and anabolic).
In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is transformed into an acetyl group attached to a carrier molecule of coenzyme A. The resulting acetyl CoA can enter several pathways, but most often, the acetyl group is delivered to the citric acid cycle for further catabolism. During the conversion of pyruvate into the acetyl group, a molecule of carbon dioxide and two high-energy electrons are removed. The carbon dioxide accounts for two (conversion of two pyruvate molecules) of the six carbons of the original glucose molecule. The electrons are picked up by NAD + , and the NADH carries the electrons to a later pathway for ATP production. At this point, the glucose molecule that originally entered cellular respiration has been completely oxidized. Chemical potential energy stored within the glucose molecule has been transferred to electron carriers or has been used to synthesize a few ATPs.
The citric acid cycle is a series of redox and decarboxylation reactions that remove high-energy electrons and carbon dioxide. The electrons temporarily stored in molecules of NADH and FADH 2 are used to generate ATP in a subsequent pathway. One molecule of either GTP or ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation on each turn of the cycle. There is no comparison of the cyclic pathway with a linear one.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?