| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
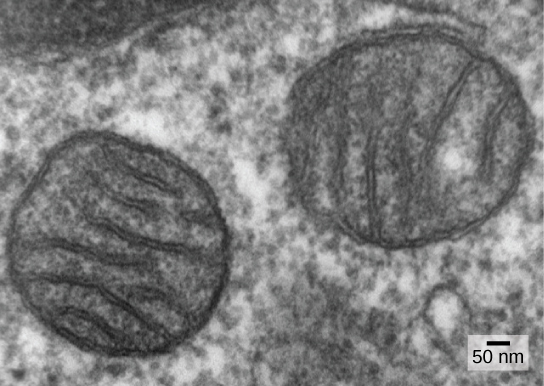
Mitochondria divide independently by a process that resembles binary fission in prokaryotes. Specifically, mitochondria are not formed from scratch (de novo) by the eukaryotic cell; they reproduce within it and are distributed with the cytoplasm when a cell divides or two cells fuse. Therefore, although these organelles are highly integrated into the eukaryotic cell, they still reproduce as if they are independent organisms within the cell. However, their reproduction is synchronized with the activity and division of the cell. Mitochondria have their own (usually) circular DNA chromosome that is stabilized by attachments to the inner membrane and carries genes similar to genes expressed by alpha-proteobacteria. Mitochondria also have special ribosomes and transfer RNAs that resemble these components in prokaryotes. These features all support that mitochondria were once free-living prokaryotes.
Mitochondria that carry out aerobic respiration have their own genomes, with genes similar to those in alpha-proteobacteria. However, many of the genes for respiratory proteins are located in the nucleus. When these genes are compared to those of other organisms, they appear to be of alpha-proteobacterial origin. Additionally, in some eukaryotic groups, such genes are found in the mitochondria, whereas in other groups, they are found in the nucleus. This has been interpreted as evidence that genes have been transferred from the endosymbiont chromosome to the host genome. This loss of genes by the endosymbiont is probably one explanation why mitochondria cannot live without a host.
Some living eukaryotes are anaerobic and cannot survive in the presence of too much oxygen. Some appear to lack organelles that could be recognized as mitochondria. In the 1970s to the early 1990s, many biologists suggested that some of these eukaryotes were descended from ancestors whose lineages had diverged from the lineage of mitochondrion-containing eukaryotes before endosymbiosis occurred. However, later findings suggest that reduced organelles are found in most, if not all, anaerobic eukaryotes, and that all eukaryotes appear to carry some genes in their nuclei that are of mitochondrial origin. In addition to the aerobic generation of ATP, mitochondria have several other metabolic functions. One of these functions is to generate clusters of iron and sulfur that are important cofactors of many enzymes. Such functions are often associated with the reduced mitochondrion-derived organelles of anaerobic eukaryotes. Therefore, most biologists accept that the last common ancestor of eukaryotes had mitochondria.
Some groups of eukaryotes are photosynthetic. Their cells contain, in addition to the standard eukaryotic organelles, another kind of organelle called a plastid . When such cells are carrying out photosynthesis, their plastids are rich in the pigment chlorophyll a and a range of other pigments, called accessory pigments, which are involved in harvesting energy from light. Photosynthetic plastids are called chloroplasts ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?