| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Androgens are sex hormones that promote masculinity. They are produced in small amounts by the adrenal cortex in both males and females. They do not affect sexual characteristics and may supplement sex hormones released from the gonads.
The adrenal medulla contains large, irregularly shaped cells that are closely associated with blood vessels. These cells are innervated by preganglionic autonomic nerve fibers from the central nervous system.
The adrenal medulla contains two types of secretory cells: one that produces epinephrine (adrenaline) and another that produces norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Epinephrine is the primary adrenal medulla hormone accounting for 75 to 80 percent of its secretions. Epinephrine and norepinephrine increase heart rate, breathing rate, cardiac muscle contractions, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels. They also accelerate the breakdown of glucose in skeletal muscles and stored fats in adipose tissue.
The release of epinephrine and norepinephrine is stimulated by neural impulses from the sympathetic nervous system. Secretion of these hormones is stimulated by acetylcholine release from preganglionic sympathetic fibers innervating the adrenal medulla. These neural impulses originate from the hypothalamus in response to stress to prepare the body for the fight-or-flight response.
The pancreas , illustrated in [link] , is an elongated organ that is located between the stomach and the proximal portion of the small intestine. It contains both exocrine cells that excrete digestive enzymes and endocrine cells that release hormones. It is sometimes referred to as a heterocrine gland because it has both endocrine and exocrine functions.
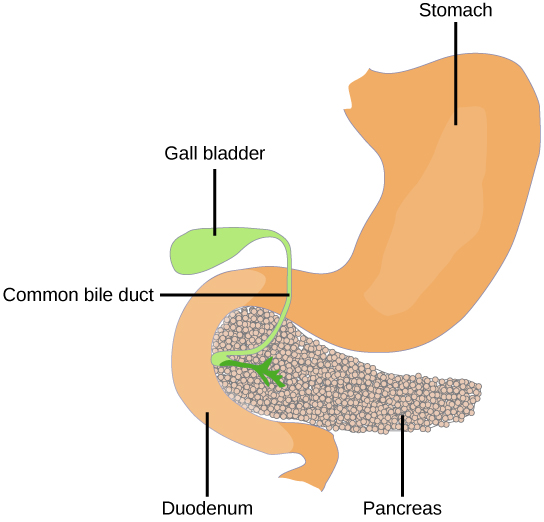
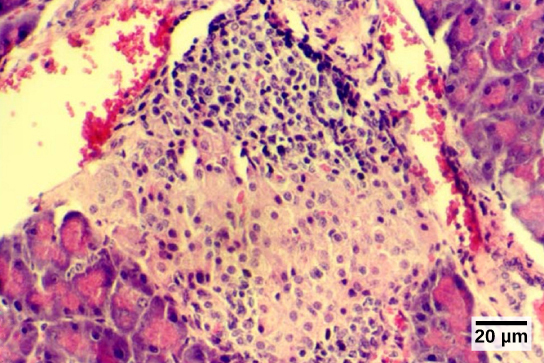
The endocrine cells of the pancreas form clusters called pancreatic islets or the islets of Langerhans , as visible in the micrograph shown in [link] . The pancreatic islets contain two primary cell types: alpha cells , which produce the hormone glucagon, and beta cells , which produce the hormone insulin. These hormones regulate blood glucose levels. As blood glucose levels decline, alpha cells release glucagon to raise the blood glucose levels by increasing rates of glycogen breakdown and glucose release by the liver. When blood glucose levels rise, such as after a meal, beta cells release insulin to lower blood glucose levels by increasing the rate of glucose uptake in most body cells, and by increasing glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscles and the liver. Together, glucagon and insulin regulate blood glucose levels.
The pineal gland produces melatonin. The rate of melatonin production is affected by the photoperiod. Collaterals from the visual pathways innervate the pineal gland. During the day photoperiod, little melatonin is produced; however, melatonin production increases during the dark photoperiod (night). In some mammals, melatonin has an inhibitory affect on reproductive functions by decreasing production and maturation of sperm, oocytes, and reproductive organs. Melatonin is an effective antioxidant, protecting the CNS from free radicals such as nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide. Lastly, melatonin is involved in biological rhythms, particularly circadian rhythms such as the sleep-wake cycle and eating habits.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?