| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Mendel’s work suggested that traits are inherited independently of each other. Morgan identified a 1:1 correspondence between a segregating trait and the X chromosome, suggesting that the random segregation of chromosomes was the physical basis of Mendel’s model. This also demonstrated that linked genes disrupt Mendel’s predicted outcomes. The fact that each chromosome can carry many linked genes explains how individuals can have many more traits than they have chromosomes. However, observations by researchers in Morgan’s laboratory suggested that alleles positioned on the same chromosome were not always inherited together. During meiosis, linked genes somehow became unlinked.
In 1909, Frans Janssen observed chiasmata—the point at which chromatids are in contact with each other and may exchange segments—prior to the first division of meiosis. He suggested that alleles become unlinked and chromosomes physically exchange segments. As chromosomes condensed and paired with their homologs, they appeared to interact at distinct points. Janssen suggested that these points corresponded to regions in which chromosome segments were exchanged. It is now known that the pairing and interaction between homologous chromosomes, known as synapsis, does more than simply organize the homologs for migration to separate daughter cells. When synapsed, homologous chromosomes undergo reciprocal physical exchanges at their arms in a process called homologous recombination , or more simply, “crossing over.”
To better understand the type of experimental results that researchers were obtaining at this time, consider a heterozygous individual that inherited dominant maternal alleles for two genes on the same chromosome (such as AB ) and two recessive paternal alleles for those same genes (such as ab ). If the genes are linked, one would expect this individual to produce gametes that are either AB or ab with a 1:1 ratio. If the genes are unlinked, the individual should produce AB , Ab , aB , and ab gametes with equal frequencies, according to the Mendelian concept of independent assortment. Because they correspond to new allele combinations, the genotypes Ab and aB are nonparental types that result from homologous recombination during meiosis. Parental types are progeny that exhibit the same allelic combination as their parents. Morgan and his colleagues, however, found that when such heterozygous individuals were test crossed to a homozygous recessive parent ( AaBb × aabb ), both parental and nonparental cases occurred. For example, 950 offspring might be recovered that were either AaBb or aabb , but 50 offspring would also be obtained that were either Aabb or aaBb . These results suggested that linkage occurred most often, but a significant minority of offspring were the products of recombination.
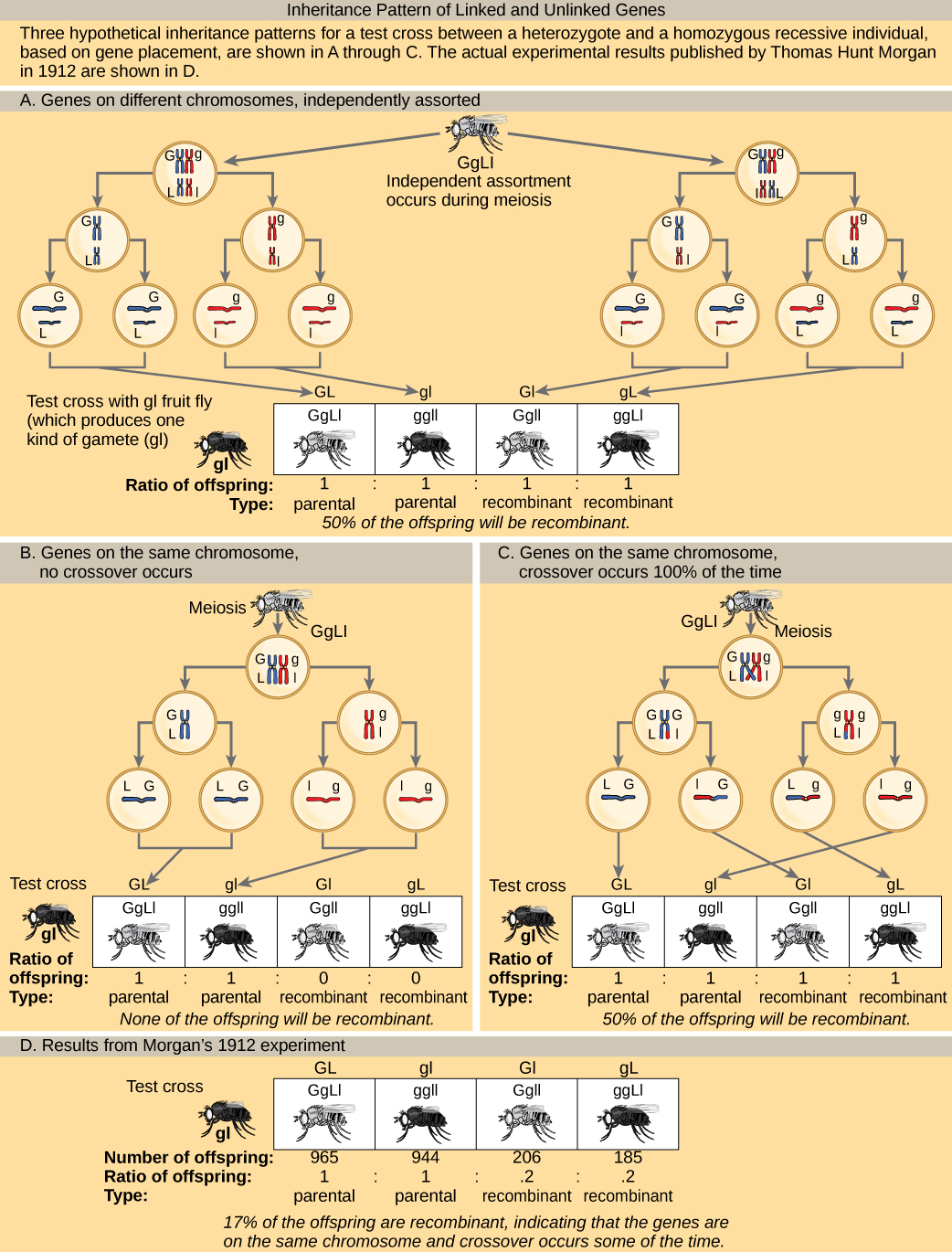
In a test cross for two characteristics such as the one shown here, can the predicted frequency of recombinant offspring be 60 percent? Why or why not?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?