| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Adenine and guanine are classified as purines . The primary structure of a purine is two carbon-nitrogen rings. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are classified as pyrimidines which have a single carbon-nitrogen ring as their primary structure ( [link] ). Each of these basic carbon-nitrogen rings has different functional groups attached to it. In molecular biology shorthand, the nitrogenous bases are simply known by their symbols A, T, G, C, and U. DNA contains A, T, G, and C whereas RNA contains A, U, G, and C.
The pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, and in RNA, the sugar is ribose ( [link] ). The difference between the sugars is the presence of the hydroxyl group on the second carbon of the ribose and hydrogen on the second carbon of the deoxyribose. The carbon atoms of the sugar molecule are numbered as 1′, 2′, 3′, 4′, and 5′ (1′ is read as “one prime”). The phosphate residue is attached to the hydroxyl group of the 5′ carbon of one sugar and the hydroxyl group of the 3′ carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, which forms a 5′–3′ phosphodiester linkage. The phosphodiester linkage is not formed by simple dehydration reaction like the other linkages connecting monomers in macromolecules: its formation involves the removal of two phosphate groups. A polynucleotide may have thousands of such phosphodiester linkages.
DNA has a double-helix structure ( [link] ). The sugar and phosphate lie on the outside of the helix, forming the backbone of the DNA. The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior, like the steps of a staircase, in pairs; the pairs are bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. Every base pair in the double helivx is separated from the next base pair by 0.34 nm. The two strands of the helix run in opposite directions, meaning that the 5′ carbon end of one strand will face the 3′ carbon end of its matching strand. (This is referred to as antiparallel orientation and is important to DNA replication and in many nucleic acid interactions.)
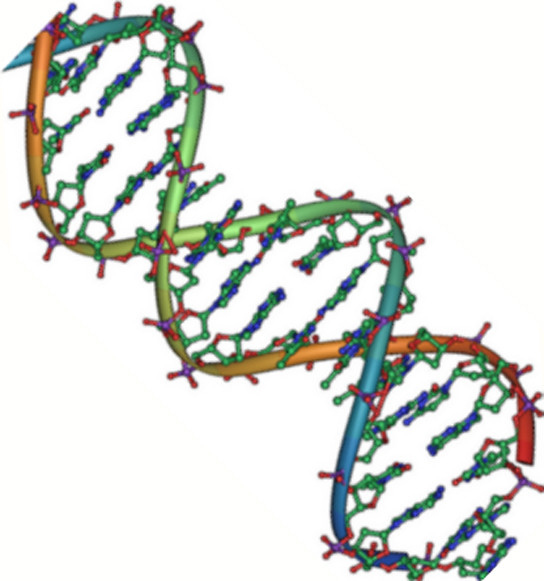
Only certain types of base pairing are allowed. For example, a certain purine can only pair with a certain pyrimidine. This means A can pair with T, and G can pair with C, as shown in [link] . This is known as the base complementary rule. In other words, the DNA strands are complementary to each other. If the sequence of one strand is AATTGGCC, the complementary strand would have the sequence TTAACCGG. During DNA replication, each strand is copied, resulting in a daughter DNA double helix containing one parental DNA strand and a newly synthesized strand.
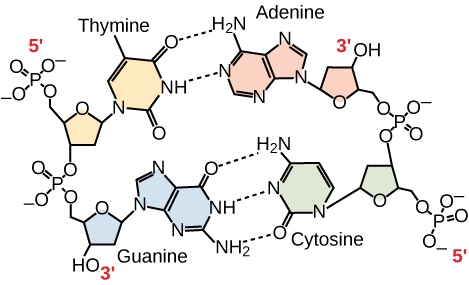
A mutation occurs, and cytosine is replaced with adenine. What impact do you think this will have on the DNA structure?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?