| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
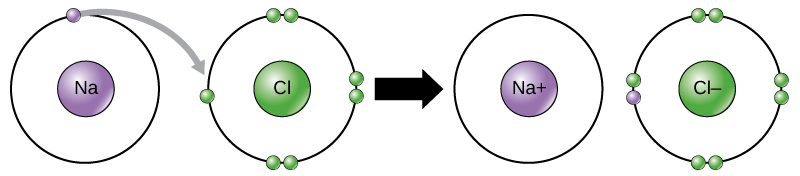
Ionic bonds are formed between ions with opposite charges. For instance, positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions bond together to make crystals of sodium chloride, or table salt, creating a crystalline molecule with zero net charge.
Certain salts are referred to in physiology as electrolytes (including sodium, potassium, and calcium), ions necessary for nerve impulse conduction, muscle contractions and water balance. Many sports drinks and dietary supplements provide these ions to replace those lost from the body via sweating during exercise.
Another way the octet rule can be satisfied is by the sharing of electrons between atoms to form covalent bonds . These bonds are stronger and much more common than ionic bonds in the molecules of living organisms. Covalent bonds are commonly found in carbon-based organic molecules, such as our DNA and proteins. Covalent bonds are also found in inorganic molecules like H 2 O, CO 2 , and O 2 . One, two, or three pairs of electrons may be shared, making single, double, and triple bonds, respectively. The more covalent bonds between two atoms, the stronger their connection. Thus, triple bonds are the strongest.
The strength of different levels of covalent bonding is one of the main reasons living organisms have a difficult time in acquiring nitrogen for use in constructing their molecules, even though molecular nitrogen, N 2 , is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere. Molecular nitrogen consists of two nitrogen atoms triple bonded to each other and, as with all molecules, the sharing of these three pairs of electrons between the two nitrogen atoms allows for the filling of their outer electron shells, making the molecule more stable than the individual nitrogen atoms. This strong triple bond makes it difficult for living systems to break apart this nitrogen in order to use it as constituents of proteins and DNA.
The formation of water molecules provides an example of covalent bonding. The hydrogen and oxygen atoms that combine to form water molecules are bound together by covalent bonds, as shown in [link] . The electron from the hydrogen splits its time between the incomplete outer shell of the hydrogen atoms and the incomplete outer shell of the oxygen atoms. To completely fill the outer shell of oxygen, which has six electrons in its outer shell but which would be more stable with eight, two electrons (one from each hydrogen atom) are needed: hence the well-known formula H 2 O. The electrons are shared between the two elements to fill the outer shell of each, making both elements more stable.
View this short video to see an animation of ionic and covalent bonding.
There are two types of covalent bonds: polar and nonpolar. In a polar covalent bond , shown in [link] , the electrons are unequally shared by the atoms and are attracted more to one nucleus than the other. Because of the unequal distribution of electrons between the atoms of different elements, a slightly positive ( δ +) or slightly negative ( δ –) charge develops. This partial charge is an important property of water and accounts for many of its characteristics.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?