| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Enzymes, proteins, electron carriers, and pumps that play roles in glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain tend to catalyze non-reversible reactions. In other words, if the initial reaction takes place, the pathway is committed to proceeding with the remaining reactions. Whether a particular enzyme activity is released depends upon the energy needs of the cell (as reflected by the levels of ATP, ADP, and AMP).
The control of glycolysis begins with the first enzyme in the pathway, hexokinase ( [link] ). This enzyme catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose, which helps to prepare the compound for cleavage in a later step. The presence of the negatively charged phosphate in the molecule also prevents the sugar from leaving the cell. When hexokinase is inhibited, glucose diffuses out of the cell and does not become a substrate for the respiration pathways in that tissue. The product of the hexokinase reaction is glucose-6-phosphate, which accumulates when a later enzyme, phosphofructokinase, is inhibited.
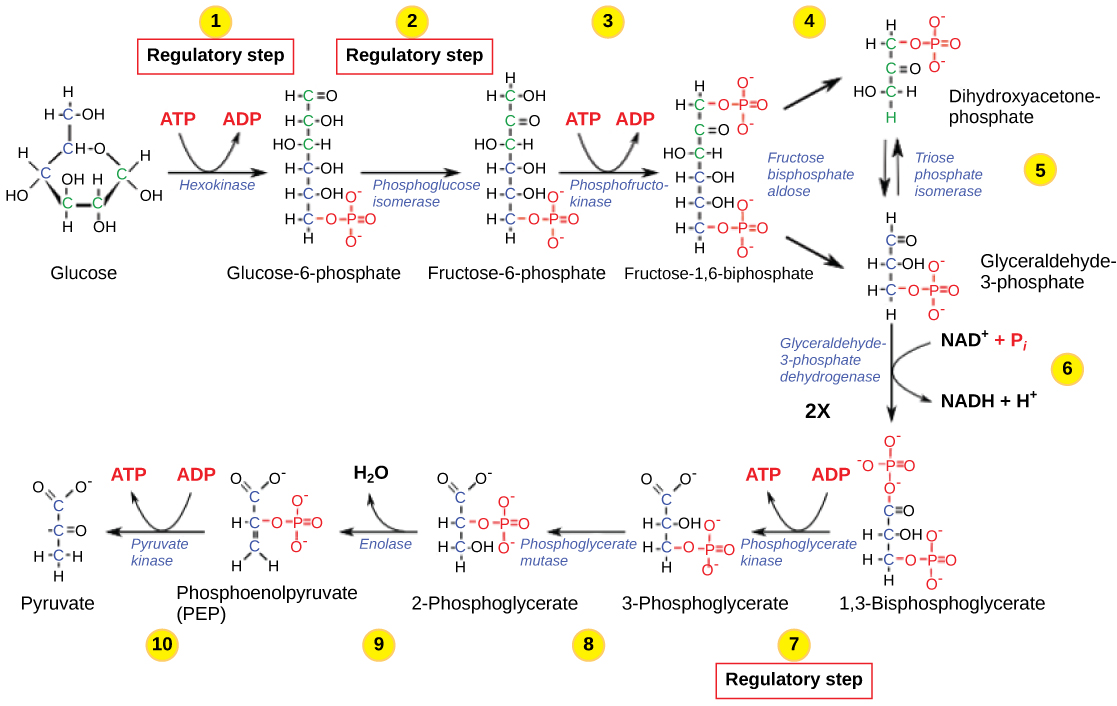
Phosphofructokinase is the main enzyme controlled in glycolysis. High levels of ATP, citrate, or a lower, more acidic pH decrease the enzyme’s activity. An increase in citrate concentration can occur because of a blockage in the citric acid cycle. Fermentation, with its production of organic acids like lactic acid, frequently accounts for the increased acidity in a cell; however, the products of fermentation do not typically accumulate in cells.
The last step in glycolysis is catalyzed by pyruvate kinase. The pyruvate produced can proceed to be catabolized or converted into the amino acid alanine. If no more energy is needed and alanine is in adequate supply, the enzyme is inhibited. The enzyme’s activity is increased when fructose-1,6-bisphosphate levels increase. (Recall that fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is an intermediate in the first half of glycolysis.) The regulation of pyruvate kinase involves phosphorylation by a kinase (pyruvate kinase kinase), resulting in a less-active enzyme. Dephosphorylation by a phosphatase reactivates it. Pyruvate kinase is also regulated by ATP (a negative allosteric effect).
If more energy is needed, more pyruvate will be converted into acetyl CoA through the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase. If either acetyl groups or NADH accumulate, there is less need for the reaction and the rate decreases. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is also regulated by phosphorylation: A kinase phosphorylates it to form an inactive enzyme, and a phosphatase reactivates it. The kinase and the phosphatase are also regulated.
The citric acid cycle is controlled through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH ( [link] ). These enzymes are isocitrate dehydrogenase and α -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. When adequate ATP and NADH levels are available, the rates of these reactions decrease. When more ATP is needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the rate increases. α -Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase will also be affected by the levels of succinyl CoA—a subsequent intermediate in the cycle—causing a decrease in activity. A decrease in the rate of operation of the pathway at this point is not necessarily negative, as the increased levels of the α -ketoglutarate not used by the citric acid cycle can be used by the cell for amino acid (glutamate) synthesis.
Specific enzymes of the electron transport chain are unaffected by feedback inhibition, but the rate of electron transport through the pathway is affected by the levels of ADP and ATP. Greater ATP consumption by a cell is indicated by a buildup of ADP. As ATP usage decreases, the concentration of ADP decreases, and now, ATP begins to build up in the cell. This change is the relative concentration of ADP to ATP triggers the cell to slow down the electron transport chain.
Visit this site to see an animation of the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis.
For a summary of feedback controls in cellular respiration, see [link] .
| Summary of Feedback Controls in Cellular Respiration | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway | Enzyme affected | Elevated levels of effector | Effect on pathway activity |
| glycolysis | hexokinase | glucose-6-phosphate | decrease |
| phosphofructokinase | low-energy charge (ATP, AMP), fructose-6-phosphate via fructose-2,6-bisphosphate | increase | |
| high-energy charge (ATP, AMP), citrate, acidic pH | decrease | ||
| pyruvate kinase | fructose-1,6-bisphosphate | increase | |
| high-energy charge (ATP, AMP), alanine | decrease | ||
| pyruvate to acetyl CoA conversion | pyruvate dehydrogenase | ADP, pyruvate | increase |
| acetyl CoA, ATP, NADH | decrease | ||
| citric acid cycle | isocitrate dehydrogenase | ADP | increase |
| ATP, NADH | decrease | ||
| α -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase | Calcium ions, ADP | increase | |
| ATP, NADH, succinyl CoA | decrease | ||
| electron transport chain | ADP | increase | |
| ATP | decrease |
Cellular respiration is controlled by a variety of means. The entry of glucose into a cell is controlled by the transport proteins that aid glucose passage through the cell membrane. Most of the control of the respiration processes is accomplished through the control of specific enzymes in the pathways. This is a type of negative feedback, turning the enzymes off. The enzymes respond most often to the levels of the available nucleosides ATP, ADP, AMP, NAD + , and FAD. Other intermediates of the pathway also affect certain enzymes in the systems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?