| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
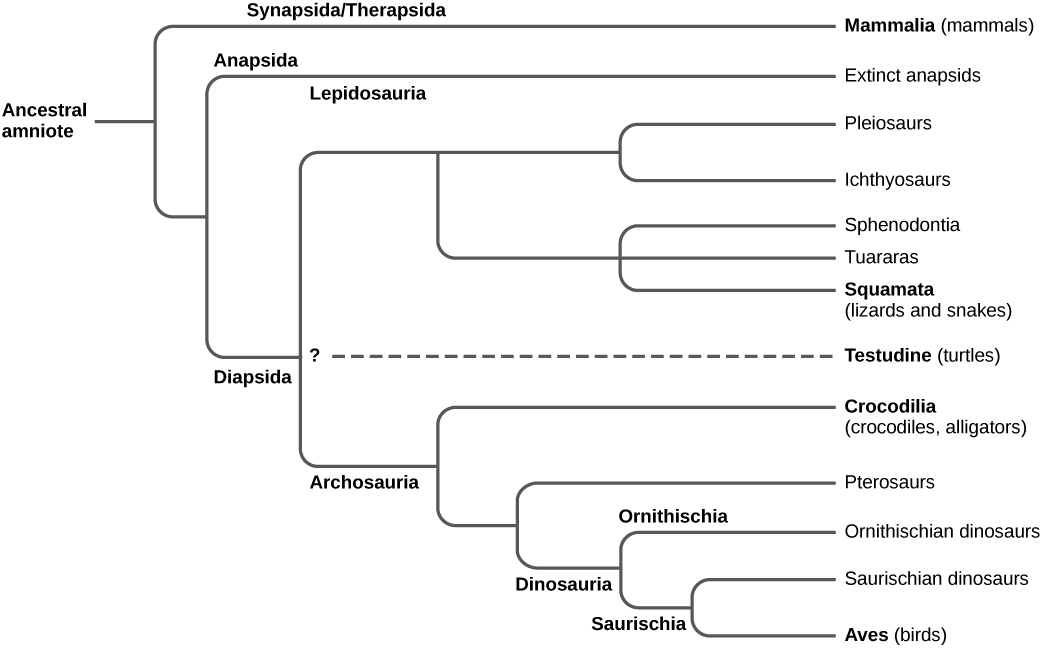
The diapsids diverged into two groups, the Archosauromorpha (“ancient lizard form”) and the Lepidosauromorpha (“scaly lizard form”) during the Mesozoic period ( [link] ). The lepidosaurs include modern lizards, snakes, and tuataras. The archosaurs include modern crocodiles and alligators, and the extinct pterosaurs (“winged lizard”) and dinosaurs (“terrible lizard”). Clade Dinosauria includes birds, which evolved from a branch of dinosaurs.
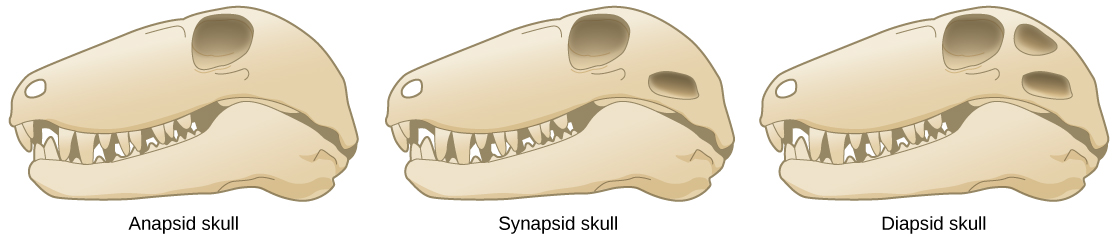
Members of the order Testudines have an anapsid-like skull with one opening. However, molecular studies indicate that turtles descended from a diapsid ancestor. Why might this be the case?
In the past, the most common division of amniotes has been into the classes Mammalia, Reptilia, and Aves. Birds are descended, however, from dinosaurs, so this classical scheme results in groups that are not true clades. We will consider birds as a group distinct from reptiles for the purpose of this discussion with the understanding that this does not completely reflect phylogenetic history and relationships.
Reptiles are tetrapods. Limbless reptiles—snakes and other squamates—have vestigial limbs and, like caecilians, are classified as tetrapods because they are descended from four-limbed ancestors. Reptiles lay eggs enclosed in shells on land. Even aquatic reptiles return to the land to lay eggs. They usually reproduce sexually with internal fertilization. Some species display ovoviviparity, with the eggs remaining in the mother’s body until they are ready to hatch. Other species are viviparous, with the offspring born alive.
One of the key adaptations that permitted reptiles to live on land was the development of their scaly skin, containing the protein keratin and waxy lipids, which reduced water loss from the skin. This occlusive skin means that reptiles cannot use their skin for respiration, like amphibians, and thus all breathe with lungs.
Reptiles are ectotherms, animals whose main source of body heat comes from the environment. This is in contrast to endotherms, which use heat produced by metabolism to regulate body temperature. In addition to being ectothermic, reptiles are categorized as poikilotherms, or animals whose body temperatures vary rather than remain stable. Reptiles have behavioral adaptations to help regulate body temperature, such as basking in sunny places to warm up and finding shady spots or going underground to cool down. The advantage of ectothermy is that metabolic energy from food is not required to heat the body; therefore, reptiles can survive on about 10 percent of the calories required by a similarly sized endotherm. In cold weather, some reptiles such as the garter snake brumate. Brumation is similar to hibernation in that the animal becomes less active and can go for long periods without eating, but differs from hibernation in that brumating reptiles are not asleep or living off fat reserves. Rather, their metabolism is slowed in response to cold temperatures, and the animal is very sluggish.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?