| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
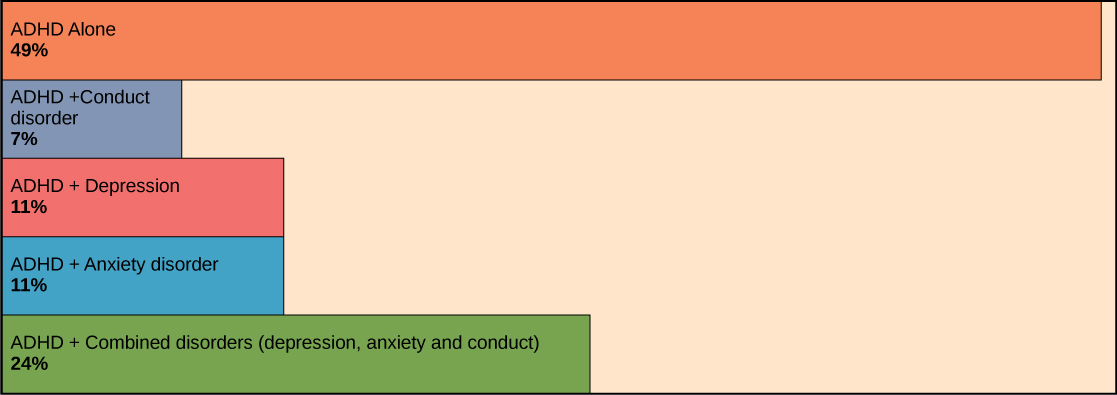
Approximately three to five percent of children and adults are affected by attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) . Like ASD, ADHD is more prevalent in males than females. Symptoms of the disorder include inattention (lack of focus), executive functioning difficulties, impulsivity, and hyperactivity beyond what is characteristic of the normal developmental stage. Some patients do not have the hyperactive component of symptoms and are diagnosed with a subtype of ADHD: attention deficit disorder (ADD). Many people with ADHD also show comorbitity, in that they develop secondary disorders in addition to ADHD. Examples include depression or obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). [link] provides some statistics concerning comorbidity with ADHD.
The cause of ADHD is unknown, although research points to a delay and dysfunction in the development of the prefrontal cortex and disturbances in neurotransmission. According to studies of twins, the disorder has a strong genetic component. There are several candidate genes that may contribute to the disorder, but no definitive links have been discovered. Environmental factors, including exposure to certain pesticides, may also contribute to the development of ADHD in some patients. Treatment for ADHD often involves behavioral therapies and the prescription of stimulant medications, which paradoxically cause a calming effect in these patients.
When examining a new patient, a neurologist takes a full medical history and performs a complete physical exam. The physical exam contains specific tasks that are used to determine what areas of the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nervous system may be damaged. For example, to check whether the hypoglossal nerve is functioning correctly, the neurologist will ask the patient to move his or her tongue in different ways. If the patient does not have full control over tongue movements, then the hypoglossal nerve may be damaged or there may be a lesion in the brainstem where the cell bodies of these neurons reside (or there could be damage to the tongue muscle itself).
Neurologists have other tools besides a physical exam they can use to diagnose particular problems in the nervous system. If the patient has had a seizure, for example, the neurologist can use electroencephalography (EEG), which involves taping electrodes to the scalp to record brain activity, to try to determine which brain regions are involved in the seizure. In suspected stroke patients, a neurologist can use a computerized tomography (CT) scan, which is a type of X-ray, to look for bleeding in the brain or a possible brain tumor. To treat patients with neurological problems, neurologists can prescribe medications or refer the patient to a neurosurgeon for surgery.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?