| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
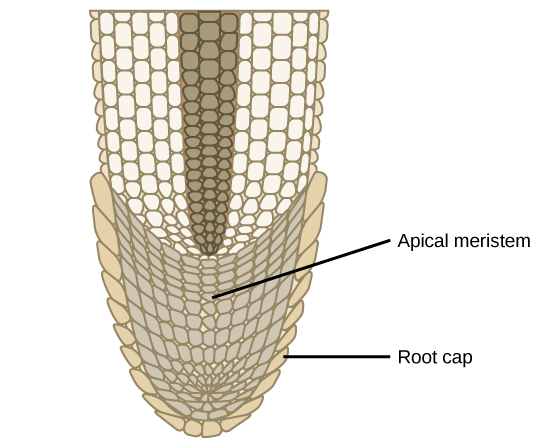
Shoots and roots of plants increase in length through rapid cell division in a tissue called the apical meristem, which is a small zone of cells found at the shoot tip or root tip ( [link] ). The apical meristem is made of undifferentiated cells that continue to proliferate throughout the life of the plant. Meristematic cells give rise to all the specialized tissues of the organism. Elongation of the shoots and roots allows a plant to access additional space and resources: light in the case of the shoot, and water and minerals in the case of roots. A separate meristem, called the lateral meristem, produces cells that increase the diameter of tree trunks.
As plants adapted to dry land and became independent from the constant presence of water in damp habitats, new organs and structures made their appearance. Early land plants did not grow more than a few inches off the ground, competing for light on these low mats. By developing a shoot and growing taller, individual plants captured more light. Because air offers substantially less support than water, land plants incorporated more rigid molecules in their stems (and later, tree trunks). In small plants such as single-celled algae, simple diffusion suffices to distribute water and nutrients throughout the organism. However, for plants to evolve larger forms, the evolution of vascular tissue for the distribution of water and solutes was a prerequisite. The vascular system contains xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem conducts water and minerals absorbed from the soil up to the shoot, while phloem transports food derived from photosynthesis throughout the entire plant. A root system evolved to take up water and minerals from the soil, and to anchor the increasingly taller shoot in the soil.
In land plants, a waxy, waterproof cover called a cuticle protects the leaves and stems from desiccation. However, the cuticle also prevents intake of carbon dioxide needed for the synthesis of carbohydrates through photosynthesis. To overcome this, stomata or pores that open and close to regulate traffic of gases and water vapor appeared in plants as they moved away from moist environments into drier habitats.
Water filters ultraviolet-B (UVB) light, which is harmful to all organisms, especially those that must absorb light to survive. This filtering does not occur for land plants. This presented an additional challenge to land colonization, which was met by the evolution of biosynthetic pathways for the synthesis of protective flavonoids and other compounds: pigments that absorb UV wavelengths of light and protect the aerial parts of plants from photodynamic damage.
Plants cannot avoid being eaten by animals. Instead, they synthesize a large range of poisonous secondary metabolites: complex organic molecules such as alkaloids, whose noxious smells and unpleasant taste deter animals. These toxic compounds can also cause severe diseases and even death, thus discouraging predation. Humans have used many of these compounds for centuries as drugs, medications, or spices. In contrast, as plants co-evolved with animals, the development of sweet and nutritious metabolites lured animals into providing valuable assistance in dispersing pollen grains, fruit, or seeds. Plants have been enlisting animals to be their helpers in this way for hundreds of millions of years.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?