| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
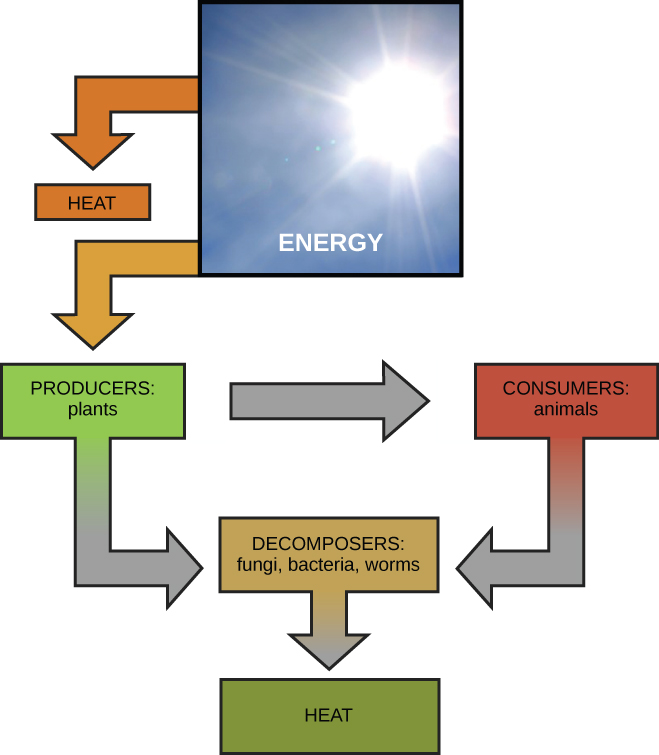
Scientists use the term bioenergetics to discuss the concept of energy flow ( [link] ) through living systems, such as cells. Cellular processes such as the building and breaking down of complex molecules occur through stepwise chemical reactions. Some of these chemical reactions are spontaneous and release energy, whereas others require energy to proceed. Just as living things must continually consume food to replenish what has been used, cells must continually produce more energy to replenish that used by the many energy-requiring chemical reactions that constantly take place. All of the chemical reactions that take place inside cells, including those that use energy and those that release energy, are the cell’s metabolism .
The metabolism of sugar (a simple carbohydrate) is a classic example of the many cellular processes that use and produce energy. Living things consume sugar as a major energy source, because sugar molecules have a great deal of energy stored within their bonds. The breakdown of glucose, a simple sugar, is described by the equation:
Carbohydrates that are consumed have their origins in photosynthesizing organisms like plants ( [link] ). During photosynthesis, plants use the energy of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide gas (CO 2 ) into sugar molecules, like glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ). Because this process involves synthesizing a larger, energy-storing molecule, it requires an input of energy to proceed. The synthesis of glucose is described by this equation (notice that it is the reverse of the previous equation):
During the chemical reactions of photosynthesis, energy is provided in the form of a very high-energy molecule called ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, which is the primary energy currency of all cells. Just as the dollar is used as currency to buy goods, cells use molecules of ATP as energy currency to perform immediate work. The sugar (glucose) is stored as starch or glycogen. Energy-storing polymers like these are broken down into glucose to supply molecules of ATP.
Solar energy is required to synthesize a molecule of glucose during the reactions of photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, light energy from the sun is initially transformed into chemical energy that is temporally stored in the energy carrier molecules ATP and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). The stored energy in ATP and NADPH is then used later in photosynthesis to build one molecule of glucose from six molecules of CO 2 . This process is analogous to eating breakfast in the morning to acquire energy for your body that can be used later in the day. Under ideal conditions, energy from 18 molecules of ATP is required to synthesize one molecule of glucose during the reactions of photosynthesis. Glucose molecules can also be combined with and converted into other types of sugars. When sugars are consumed, molecules of glucose eventually make their way into each living cell of the organism. Inside the cell, each sugar molecule is broken down through a complex series of chemical reactions. The goal of these reactions is to harvest the energy stored inside the sugar molecules. The harvested energy is used to make high-energy ATP molecules, which can be used to perform work, powering many chemical reactions in the cell. The amount of energy needed to make one molecule of glucose from six molecules of carbon dioxide is 18 molecules of ATP and 12 molecules of NADPH (each one of which is energetically equivalent to three molecules of ATP), or a total of 54 molecule equivalents required for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose. This process is a fundamental and efficient way for cells to generate the molecular energy that they require.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?