| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient—that is, if the concentration of the substance inside the cell is greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid (and vice versa)—the cell must use energy to move the substance. Some active transport mechanisms move small-molecular weight materials, such as ions, through the membrane. Other mechanisms transport much larger molecules.
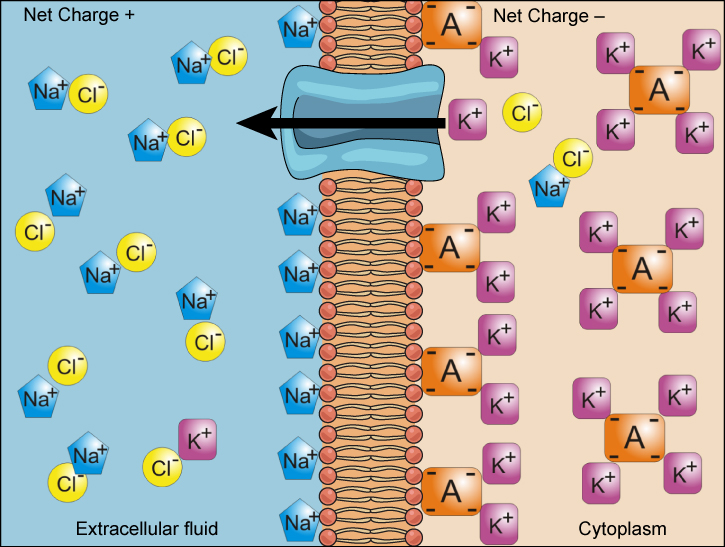
We have discussed simple concentration gradients—differential concentrations of a substance across a space or a membrane—but in living systems, gradients are more complex. Because ions move into and out of cells and because cells contain proteins that do not move across the membrane and are mostly negatively charged, there is also an electrical gradient, a difference of charge, across the plasma membrane. The interior of living cells is electrically negative with respect to the extracellular fluid in which they are bathed, and at the same time, cells have higher concentrations of potassium (K + ) and lower concentrations of sodium (Na + ) than does the extracellular fluid. So in a living cell, the concentration gradient of Na + tends to drive it into the cell, and the electrical gradient of Na + (a positive ion) also tends to drive it inward to the negatively charged interior. The situation is more complex, however, for other elements such as potassium. The electrical gradient of K + , a positive ion, also tends to drive it into the cell, but the concentration gradient of K + tends to drive K + out of the cell ( [link] ). The combined gradient of concentration and electrical charge that affects an ion is called its electrochemical gradient .
Injection of a potassium solution into a person’s blood is lethal; this is used in capital punishment and euthanasia. Why do you think a potassium solution injection is lethal?
To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, the cell must use energy. This energy is harvested from ATP generated through the cell’s metabolism. Active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps , work against electrochemical gradients. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive movements. Much of a cell’s supply of metabolic energy may be spent maintaining these processes. (Most of a red blood cell’s metabolic energy is used to maintain the imbalance between exterior and interior sodium and potassium levels required by the cell.) Because active transport mechanisms depend on a cell’s metabolism for energy, they are sensitive to many metabolic poisons that interfere with the supply of ATP.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?