| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The process in which an organism develops from a single-celled zygote to a multi-cellular organism is complex and well-regulated. The early stages of embryonic development are also crucial for ensuring the fitness of the organism.
Fertilization, pictured in [link] a is the process in which gametes (an egg and sperm) fuse to form a zygote. The egg and sperm each contain one set of chromosomes. To ensure that the offspring has only one complete diploid set of chromosomes, only one sperm must fuse with one egg. In mammals, the egg is protected by a layer of extracellular matrix consisting mainly of glycoproteins called the zona pellucida . When a sperm binds to the zona pellucida, a series of biochemical events, called the acrosomal reactions , take place. In placental mammals, the acrosome contains digestive enzymes that initiate the degradation of the glycoprotein matrix protecting the egg and allowing the sperm plasma membrane to fuse with the egg plasma membrane, as illustrated in [link] b . The fusion of these two membranes creates an opening through which the sperm nucleus is transferred into the ovum. The nuclear membranes of the egg and sperm break down and the two haploid genomes condense to form a diploid genome.
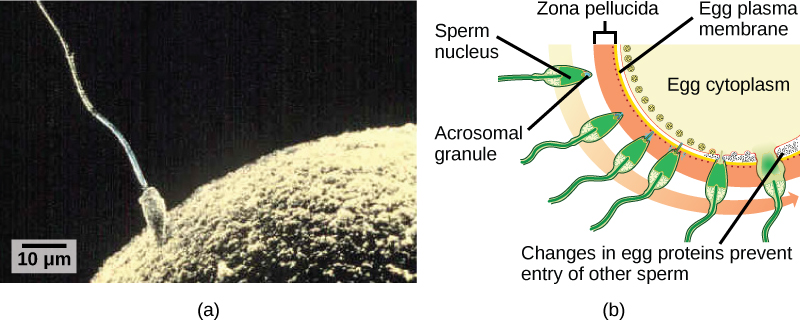
To ensure that no more than one sperm fertilizes the egg, once the acrosomal reactions take place at one location of the egg membrane, the egg releases proteins in other locations to prevent other sperm from fusing with the egg. If this mechanism fails, multiple sperm can fuse with the egg, resulting in polyspermy . The resulting embryo is not genetically viable and dies within a few days.
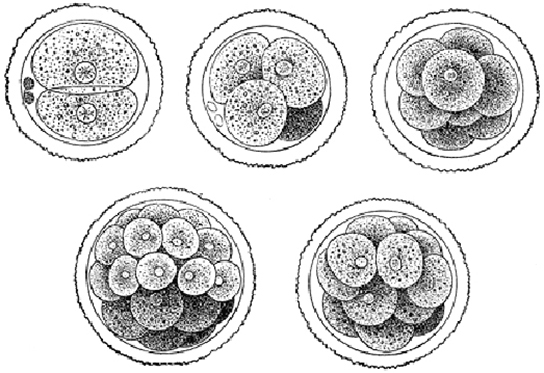
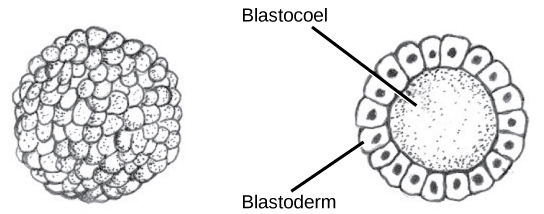
The development of multi-cellular organisms begins from a single-celled zygote, which undergoes rapid cell division to form the blastula. The rapid, multiple rounds of cell division are termed cleavage. Cleavage is illustrated in ( [link] a ). After the cleavage has produced over 100 cells, the embryo is called a blastula. The blastula is usually a spherical layer of cells (the blastoderm) surrounding a fluid-filled or yolk-filled cavity (the blastocoel). Mammals at this stage form a structure called the blastocyst, characterized by an inner cell mass that is distinct from the surrounding blastula, shown in [link] b . During cleavage, the cells divide without an increase in mass; that is, one large single-celled zygote divides into multiple smaller cells. Each cell within the blastula is called a blastomere.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?