| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Of the four major macromolecules in biological systems, both proteins and nucleic acids contain nitrogen. During the catabolism, or breakdown, of nitrogen-containing macromolecules, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are extracted and stored in the form of carbohydrates and fats. Excess nitrogen is excreted from the body. Nitrogenous wastes tend to form toxic ammonia , which raises the pH of body fluids. The formation of ammonia itself requires energy in the form of ATP and large quantities of water to dilute it out of a biological system. Animals that live in aquatic environments tend to release ammonia into the water. Animals that excrete ammonia are said to be ammonotelic . Terrestrial organisms have evolved other mechanisms to excrete nitrogenous wastes. The animals must detoxify ammonia by converting it into a relatively nontoxic form such as urea or uric acid. Mammals, including humans, produce urea, whereas reptiles and many terrestrial invertebrates produce uric acid. Animals that secrete urea as the primary nitrogenous waste material are called ureotelic animals.
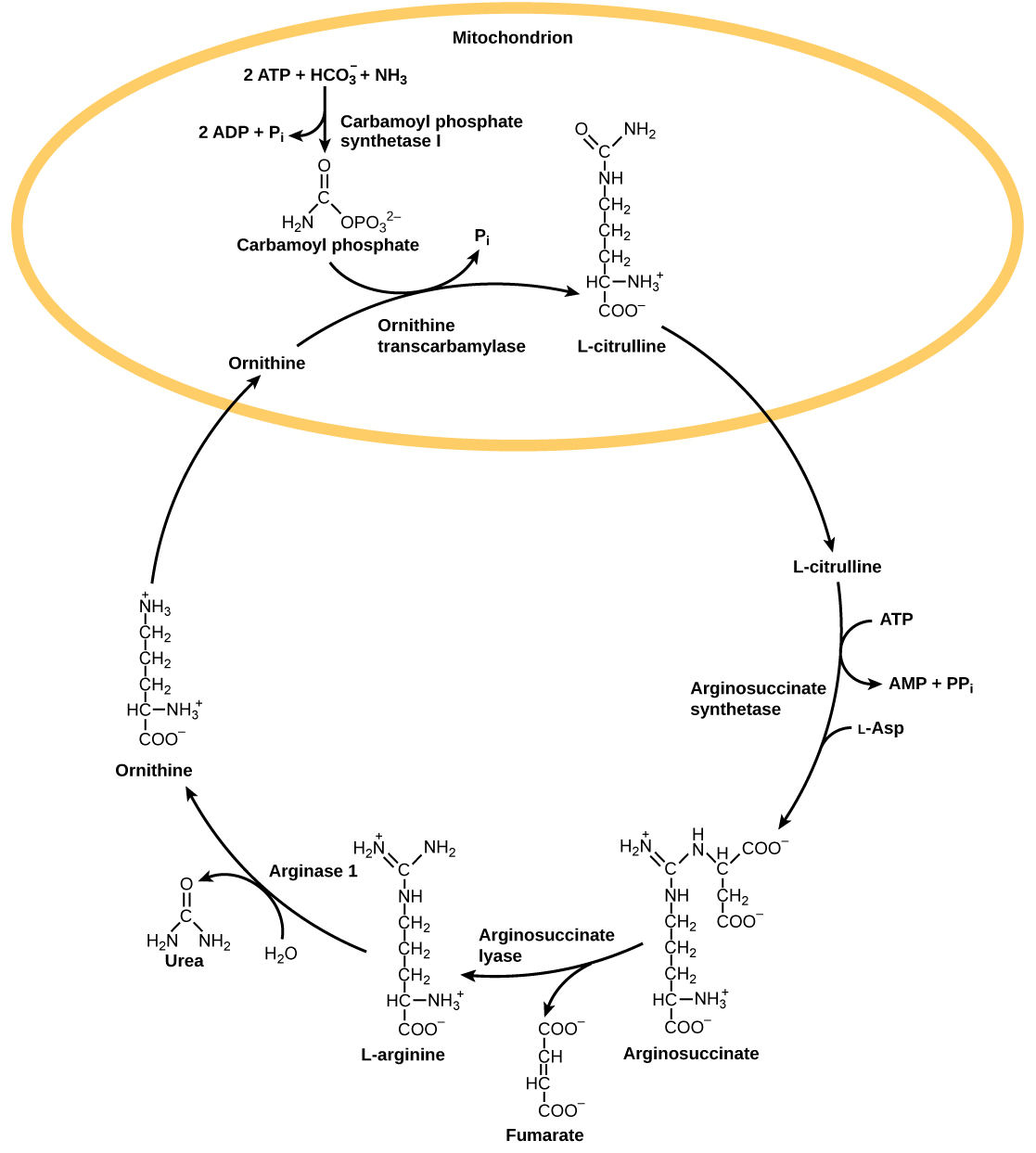
The urea cycle is the primary mechanism by which mammals convert ammonia to urea. Urea is made in the liver and excreted in urine. The overall chemical reaction by which ammonia is converted to urea is 2 NH 3 (ammonia) + CO 2 + 3 ATP + H 2 O → H 2 N-CO-NH 2 (urea) + 2 ADP + 4 P i + AMP.
The urea cycle utilizes five intermediate steps, catalyzed by five different enzymes, to convert ammonia to urea, as shown in [link] . The amino acid L-ornithine gets converted into different intermediates before being regenerated at the end of the urea cycle. Hence, the urea cycle is also referred to as the ornithine cycle. The enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase catalyzes a key step in the urea cycle and its deficiency can lead to accumulation of toxic levels of ammonia in the body. The first two reactions occur in the mitochondria and the last three reactions occur in the cytosol. Urea concentration in the blood, called blood urea nitrogen or BUN, is used as an indicator of kidney function.
Birds, reptiles, and most terrestrial arthropods convert toxic ammonia to uric acid or the closely related compound guanine (guano) instead of urea. Mammals also form some uric acid during breakdown of nucleic acids. Uric acid is a compound similar to purines found in nucleic acids. It is water insoluble and tends to form a white paste or powder; it is excreted by birds, insects, and reptiles. Conversion of ammonia to uric acid requires more energy and is much more complex than conversion of ammonia to urea [link] .
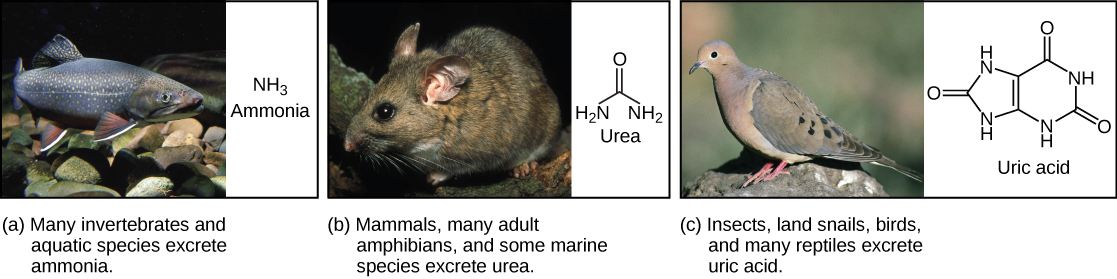
Ammonia is the waste produced by metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds like proteins and nucleic acids. While aquatic animals can easily excrete ammonia into their watery surroundings, terrestrial animals have evolved special mechanisms to eliminate the toxic ammonia from their systems. Urea is the major byproduct of ammonia metabolism in vertebrate animals. Uric acid is the major byproduct of ammonia metabolism in birds, terrestrial arthropods, and reptiles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?