| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Once the oxygen diffuses across the alveoli, it enters the bloodstream and is transported to the tissues where it is unloaded, and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood and into the alveoli to be expelled from the body. Although gas exchange is a continuous process, the oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported by different mechanisms.
Although oxygen dissolves in blood, only a small amount of oxygen is transported this way. Only 1.5 percent of oxygen in the blood is dissolved directly into the blood itself. Most oxygen—98.5 percent—is bound to a protein called hemoglobin and carried to the tissues.
Hemoglobin , or Hb, is a protein molecule found in red blood cells (erythrocytes) made of four subunits: two alpha subunits and two beta subunits ( [link] ). Each subunit surrounds a central heme group that contains iron and binds one oxygen molecule, allowing each hemoglobin molecule to bind four oxygen molecules. Molecules with more oxygen bound to the heme groups are brighter red. As a result, oxygenated arterial blood where the Hb is carrying four oxygen molecules is bright red, while venous blood that is deoxygenated is darker red.
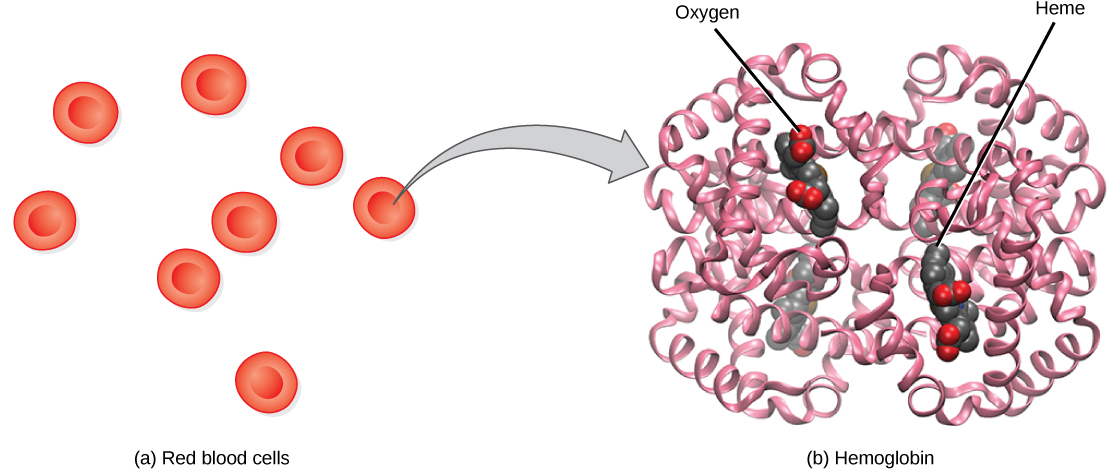
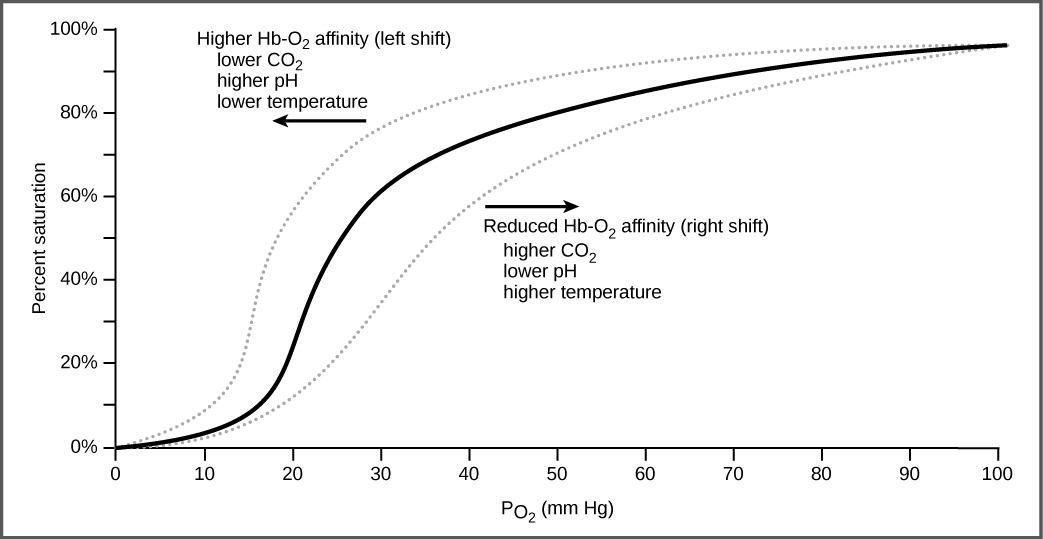
It is easier to bind a second and third oxygen molecule to Hb than the first molecule. This is because the hemoglobin molecule changes its shape, or conformation, as oxygen binds. The fourth oxygen is then more difficult to bind. The binding of oxygen to hemoglobin can be plotted as a function of the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood (x-axis) versus the relative Hb-oxygen saturation (y-axis). The resulting graph—an oxygen dissociation curve —is sigmoidal, or S-shaped ( [link] ). As the partial pressure of oxygen increases, the hemoglobin becomes increasingly saturated with oxygen.
The kidneys are responsible for removing excess H+ ions from the blood. If the kidneys fail, what would happen to blood pH and to hemoglobin affinity for oxygen?
The oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin determines how much oxygen is carried in the blood. In addition to , other environmental factors and diseases can affect oxygen carrying capacity and delivery.
Carbon dioxide levels, blood pH, and body temperature affect oxygen-carrying capacity ( [link] ). When carbon dioxide is in the blood, it reacts with water to form bicarbonate and hydrogen ions (H + ). As the level of carbon dioxide in the blood increases, more H + is produced and the pH decreases. This increase in carbon dioxide and subsequent decrease in pH reduce the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. The oxygen dissociates from the Hb molecule, shifting the oxygen dissociation curve to the right. Therefore, more oxygen is needed to reach the same hemoglobin saturation level as when the pH was higher. A similar shift in the curve also results from an increase in body temperature. Increased temperature, such as from increased activity of skeletal muscle, causes the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen to be reduced.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?