| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The most obvious characteristic that sets birds apart from other modern vertebrates is the presence of feathers, which are modified scales. While vertebrates like bats fly without feathers, birds rely on feathers and wings, along with other modifications of body structure and physiology, for flight.
Birds are endothermic, and because they fly, they require large amounts of energy, necessitating a high metabolic rate. Like mammals, which are also endothermic, birds have an insulating covering that keeps heat in the body: feathers. Specialized feathers called down feathers are especially insulating, trapping air in spaces between each feather to decrease the rate of heat loss. Certain parts of a bird’s body are covered in down feathers, and the base of other feathers have a downy portion, whereas newly hatched birds are covered in down.
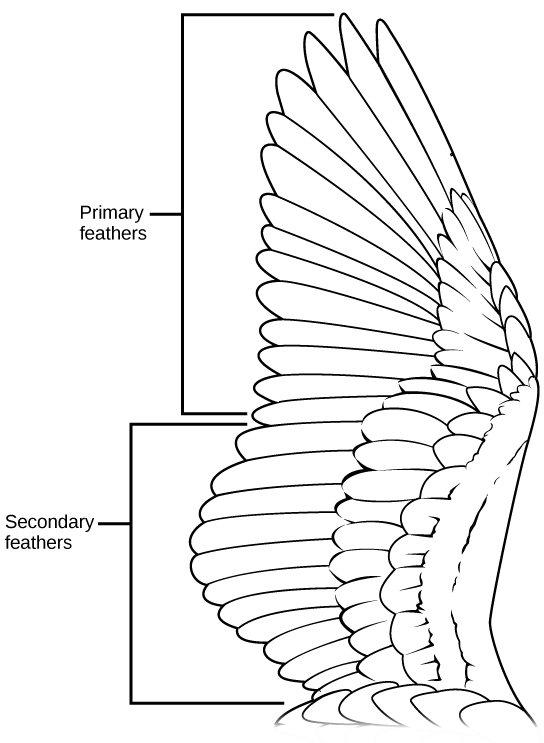
Feathers not only act as insulation but also allow for flight, enabling the lift and thrust necessary to become airborne. The feathers on a wing are flexible, so the collective feathers move and separate as air moves through them, reducing the drag on the wing. Flight feathers are asymmetrical, which affects airflow over them and provides some of the lifting and thrusting force required for flight ( [link] ). Two types of flight feathers are found on the wings, primary feathers and secondary feathers. Primary feathers are located at the tip of the wing and provide thrust. Secondary feathers are located closer to the body, attach to the forearm portion of the wing and provide lift. Contour feathers are the feathers found on the body, and they help reduce drag produced by wind resistance during flight. They create a smooth, aerodynamic surface so that air moves smoothly over the bird’s body, allowing for efficient flight.
Flapping of the entire wing occurs primarily through the actions of the chest muscles, the pectoralis and the supracoracoideus. These muscles are highly developed in birds and account for a higher percentage of body mass than in most mammals. These attach to a blade-shaped keel, like that of a boat, located on the sternum. The sternum of birds is larger than that of other vertebrates, which accommodates the large muscles required to generate enough upward force to generate lift with the flapping of the wings. Another skeletal modification found in most birds is the fusion of the two clavicles (collarbones), forming the furcula or wishbone. The furcula is flexible enough to bend and provide support to the shoulder girdle during flapping.
An important requirement of flight is a low body weight. As body weight increases, the muscle output required for flying increases. The largest living bird is the ostrich, and while it is much smaller than the largest mammals, it is flightless. For birds that do fly, reduction in body weight makes flight easier. Several modifications are found in birds to reduce body weight, including pneumatization of bones. Pneumatic bones are bones that are hollow, rather than filled with tissue ( [link] ). They contain air spaces that are sometimes connected to air sacs, and they have struts of bone to provide structural reinforcement. Pneumatic bones are not found in all birds, and they are more extensive in large birds than in small birds. Not all bones of the skeleton are pneumatic, although the skulls of almost all birds are.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?