| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The amniotes —reptiles, birds, and mammals—are distinguished from amphibians by their terrestrially adapted egg, which is protected by amniotic membranes. The evolution of amniotic membranes meant that the embryos of amniotes were provided with their own aquatic environment, which led to less dependence on water for development and thus allowed the amniotes to branch out into drier environments. This was a significant development that distinguished them from amphibians, which were restricted to moist environments due their shell-less eggs. Although the shells of various amniotic species vary significantly, they all allow retention of water. The shells of bird eggs are composed of calcium carbonate and are hard, but fragile. The shells of reptile eggs are leathery and require a moist environment. Most mammals do not lay eggs (except for monotremes). Instead, the embryo grows within the mother’s body; however, even with this internal gestation, amniotic membranes are still present.
The amniotic egg is the key characteristic of amniotes. In amniotes that lay eggs, the shell of the egg provides protection for the developing embryo while being permeable enough to allow for the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen. The albumin, or egg white, provides the embryo with water and protein, whereas the fattier egg yolk is the energy supply for the embryo, as is the case with the eggs of many other animals, such as amphibians. However, the eggs of amniotes contain three additional extra-embryonic membranes: the chorion, amnion, and allantois ( [link] ). Extra-embryonic membranes are membranes present in amniotic eggs that are not a part of the body of the developing embryo. While the inner amniotic membrane surrounds the embryo itself, the chorion surrounds the embryo and yolk sac. The chorion facilitates exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the embryo and the egg’s external environment. The amnion protects the embryo from mechanical shock and supports hydration. The allantois stores nitrogenous wastes produced by the embryo and also facilitates respiration. In mammals, membranes that are homologous to the extra-embryonic membranes in eggs are present in the placenta.
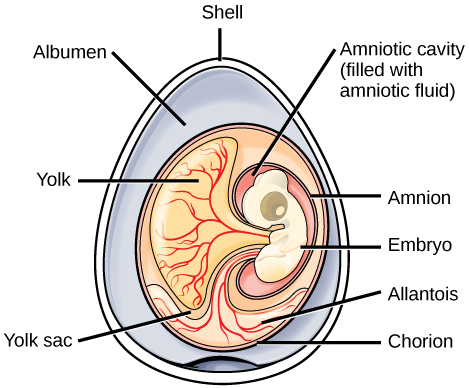
Which of the following statements about the parts of an egg are false?
Additional derived characteristics of amniotes include waterproof skin, due to the presence of lipids, and costal (rib) ventilation of the lungs.
The first amniotes evolved from amphibian ancestors approximately 340 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. The early amniotes diverged into two main lines soon after the first amniotes arose. The initial split was into synapsids and sauropsids. Synapsids include all mammals, including extinct mammalian species. Synapsids also include therapsids, which were mammal-like reptiles from which mammals evolved. Sauropsids include reptiles and birds, and can be further divided into anapsids and diapsids. The key differences between the synapsids, anapsids, and diapsids are the structures of the skull and the number of temporal fenestrae behind each eye ( [link] ). Temporal fenestrae are post-orbital openings in the skull that allow muscles to expand and lengthen. Anapsids have no temporal fenestrae, synapsids have one, and diapsids have two. Anapsids include extinct organisms and may, based on anatomy, include turtles. However, this is still controversial, and turtles are sometimes classified as diapsids based on molecular evidence. The diapsids include birds and all other living and extinct reptiles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?