| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
DNA replication is a highly accurate process, but mistakes can occasionally occur, such as a DNA polymerase inserting a wrong base. Uncorrected mistakes may sometimes lead to serious consequences, such as cancer. Repair mechanisms correct the mistakes. In rare cases, mistakes are not corrected, leading to mutations; in other cases, repair enzymes are themselves mutated or defective.
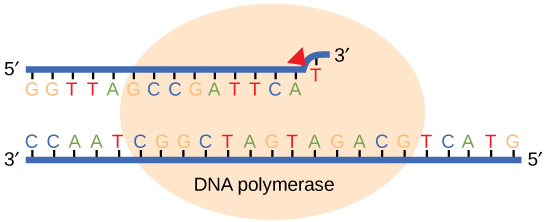
Most of the mistakes during DNA replication are promptly corrected by DNA polymerase by proofreading the base that has been just added ( [link] ). In proofreading , the DNA pol reads the newly added base before adding the next one, so a correction can be made. The polymerase checks whether the newly added base has paired correctly with the base in the template strand. If it is the right base, the next nucleotide is added. If an incorrect base has been added, the enzyme makes a cut at the phosphodiester bond and releases the wrong nucleotide. This is performed by the exonuclease action of DNA pol III. Once the incorrect nucleotide has been removed, a new one will be added again.
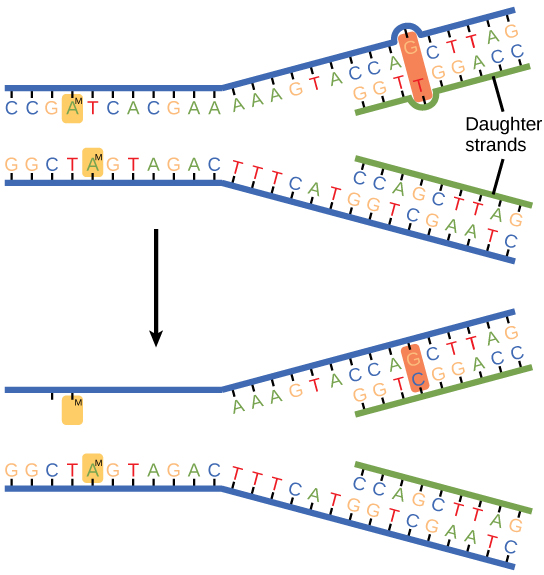
Some errors are not corrected during replication, but are instead corrected after replication is completed; this type of repair is known as mismatch repair ( [link] ). The enzymes recognize the incorrectly added nucleotide and excise it; this is then replaced by the correct base. If this remains uncorrected, it may lead to more permanent damage. How do mismatch repair enzymes recognize which of the two bases is the incorrect one? In E. coli , after replication, the nitrogenous base adenine acquires a methyl group; the parental DNA strand will have methyl groups, whereas the newly synthesized strand lacks them. Thus, DNA polymerase is able to remove the wrongly incorporated bases from the newly synthesized, non-methylated strand. In eukaryotes, the mechanism is not very well understood, but it is believed to involve recognition of unsealed nicks in the new strand, as well as a short-term continuing association of some of the replication proteins with the new daughter strand after replication has completed.
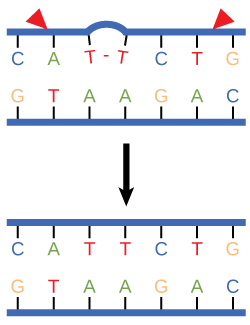
In another type of repair mechanism, nucleotide excision repair , enzymes replace incorrect bases by making a cut on both the 3' and 5' ends of the incorrect base ( [link] ). The segment of DNA is removed and replaced with the correctly paired nucleotides by the action of DNA pol. Once the bases are filled in, the remaining gap is sealed with a phosphodiester linkage catalyzed by DNA ligase. This repair mechanism is often employed when UV exposure causes the formation of pyrimidine dimers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?