| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The elucidation of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how DNA divides and makes copies of itself. This model suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. What was not clear was how the replication took place. There were three models suggested ( [link] ): conservative, semi-conservative, and dispersive.
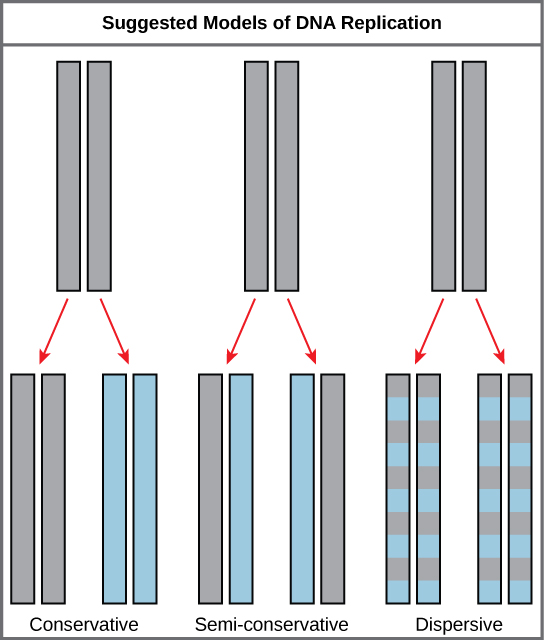
In conservative replication, the parental DNA remains together, and the newly formed daughter strands are together. The semi-conservative method suggests that each of the two parental DNA strands act as a template for new DNA to be synthesized; after replication, each double-stranded DNA includes one parental or “old” strand and one “new” strand. In the dispersive model, both copies of DNA have double-stranded segments of parental DNA and newly synthesized DNA interspersed.
Meselson and Stahl were interested in understanding how DNA replicates. They grew E. coli for several generations in a medium containing a “heavy” isotope of nitrogen ( 15 N) that gets incorporated into nitrogenous bases, and eventually into the DNA ( [link] ).
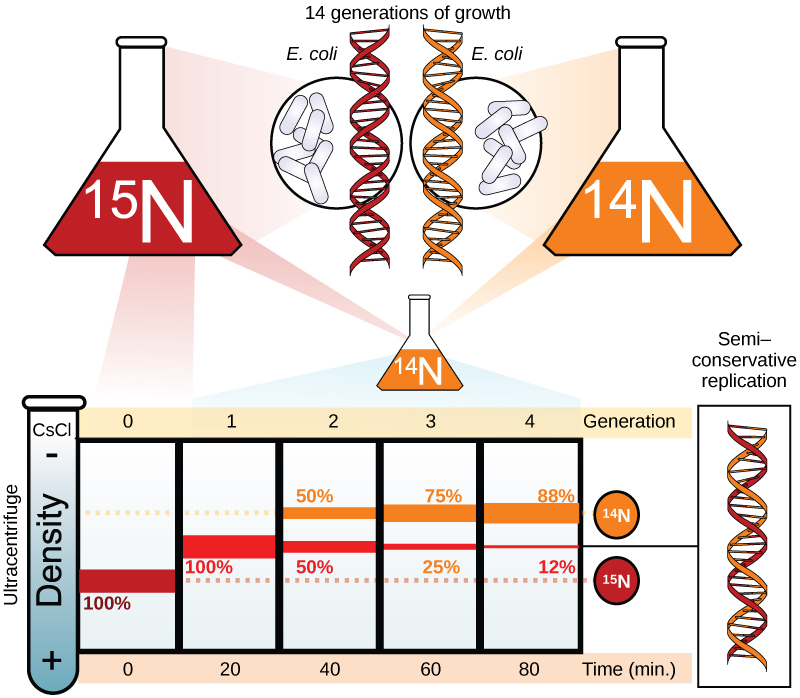
The E. coli culture was then shifted into medium containing 14 N and allowed to grow for one generation. The cells were harvested and the DNA was isolated. The DNA was centrifuged at high speeds in an ultracentrifuge. Some cells were allowed to grow for one more life cycle in 14 N and spun again. During the density gradient centrifugation, the DNA is loaded into a gradient (typically a salt such as cesium chloride or sucrose) and spun at high speeds of 50,000 to 60,000 rpm. Under these circumstances, the DNA will form a band according to its density in the gradient. DNA grown in 15 N will band at a higher density position than that grown in 14 N. Meselson and Stahl noted that after one generation of growth in 14 N after they had been shifted from 15 N, the single band observed was intermediate in position in between DNA of cells grown exclusively in 15 N and 14 N. This suggested either a semi-conservative or dispersive mode of replication. The DNA harvested from cells grown for two generations in 14 N formed two bands: one DNA band was at the intermediate position between 15 N and 14 N, and the other corresponded to the band of 14 N DNA. These results could only be explained if DNA replicates in a semi-conservative manner. Therefore, the other two modes were ruled out.
During DNA replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. When two daughter DNA copies are formed, they have the same sequence and are divided equally into the two daughter cells.
Click through this tutorial on DNA replication.
The model for DNA replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. In conservative replication, the parental DNA is conserved, and the daughter DNA is newly synthesized. The semi-conservative method suggests that each of the two parental DNA strands acts as template for new DNA to be synthesized; after replication, each double-stranded DNA includes one parental or “old” strand and one “new” strand. The dispersive mode suggested that the two copies of the DNA would have segments of parental DNA and newly synthesized DNA.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?