| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
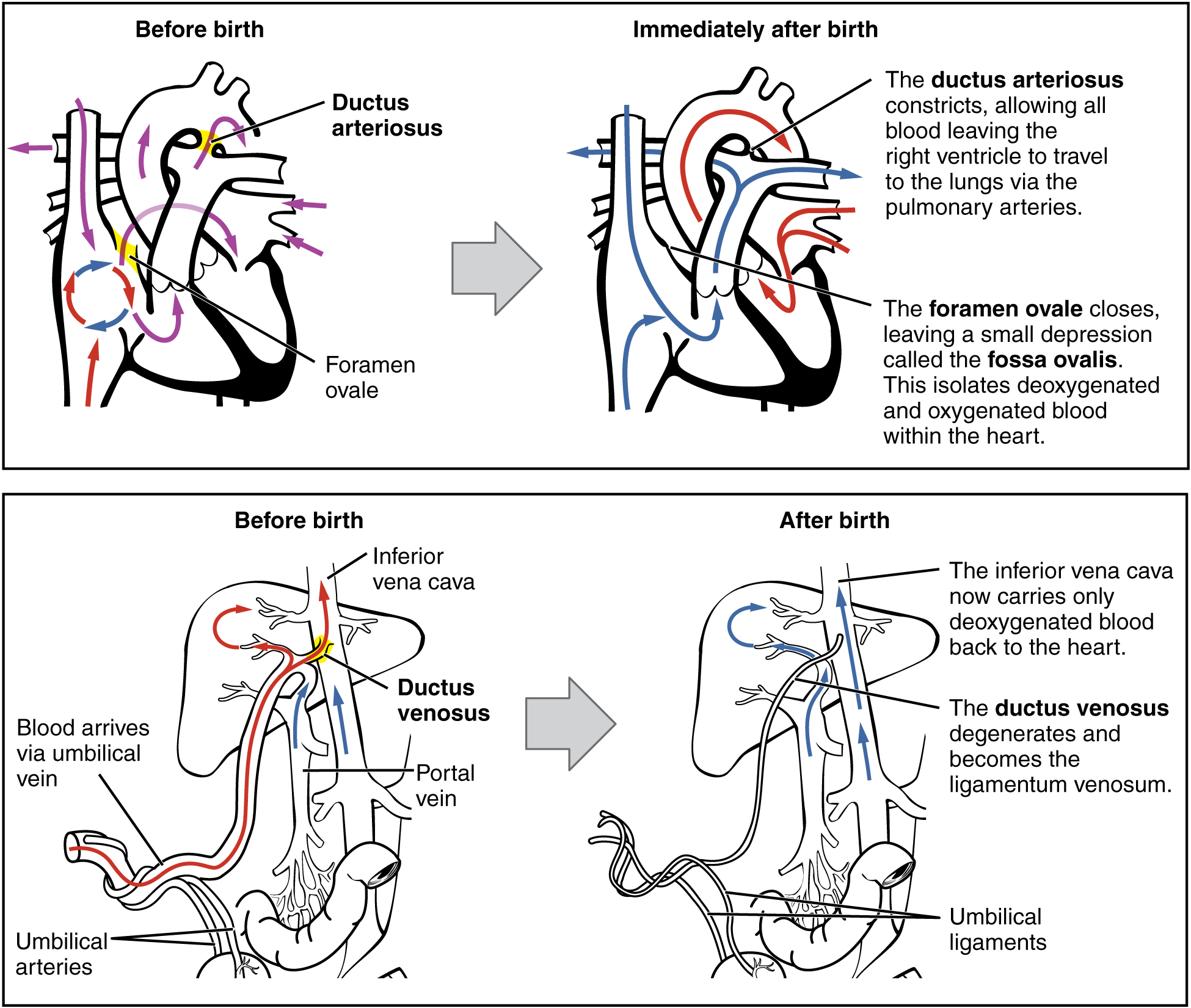
The newborn’s first breath is vital to initiate the transition from the fetal to the neonatal circulatory pattern. Inflation of the lungs decreases blood pressure throughout the pulmonary system, as well as in the right atrium and ventricle. In response to this pressure change, the flow of blood temporarily reverses direction through the foramen ovale, moving from the left to the right atrium, and blocking the shunt with two flaps of tissue. Within 1 year, the tissue flaps usually fuse over the shunt, turning the foramen ovale into the fossa ovalis. The ductus arteriosus constricts as a result of increased oxygen concentration, and becomes the ligamentum arteriosum. Closing of the ductus arteriosus ensures that all blood pumped to the pulmonary circuit will be oxygenated by the newly functional neonatal lungs.
The fetus floats in warm amniotic fluid that is maintained at a temperature of approximately 98.6°F with very little fluctuation. Birth exposes newborns to a cooler environment in which they have to regulate their own body temperature. Newborns have a higher ratio of surface area to volume than adults. This means that their body has less volume throughout which to produce heat, and more surface area from which to lose heat. As a result, newborns produce heat more slowly and lose it more quickly. Newborns also have immature musculature that limits their ability to generate heat by shivering. Moreover, their nervous systems are underdeveloped, so they cannot quickly constrict superficial blood vessels in response to cold. They also have little subcutaneous fat for insulation. All these factors make it harder for newborns to maintain their body temperature.
Newborns, however, do have a special method for generating heat: nonshivering thermogenesis , which involves the breakdown of brown adipose tissue , or brown fat, which is distributed over the back, chest, and shoulders. Brown fat differs from the more familiar white fat in two ways:
The breakdown of brown fat occurs automatically upon exposure to cold, so it is an important heat regulator in newborns. During fetal development, the placenta secretes inhibitors that prevent metabolism of brown adipose fat and promote its accumulation in preparation for birth.
In adults, the gastrointestinal tract harbors bacterial flora—trillions of bacteria that aid in digestion, produce vitamins, and protect from the invasion or replication of pathogens. In stark contrast, the fetal intestine is sterile. The first consumption of breast milk or formula floods the neonatal gastrointestinal tract with beneficial bacteria that begin to establish the bacterial flora.
The fetal kidneys filter blood and produce urine, but the neonatal kidneys are still immature and inefficient at concentrating urine. Therefore, newborns produce very dilute urine, making it particularly important for infants to obtain sufficient fluids from breast milk or formula.
Five criteria—skin color, heart rate, reflex, muscle tone, and respiration—are assessed, and each criterion is assigned a score of 0, 1, or 2. Scores are taken at 1 minute after birth and again at 5 minutes after birth. Each time that scores are taken, the five scores are added together. High scores (out of a possible 10) indicate the baby has made the transition from the womb well, whereas lower scores indicate that the baby may be in distress.
The technique for determining an Apgar score is quick and easy, painless for the newborn, and does not require any instruments except for a stethoscope. A convenient way to remember the five scoring criteria is to apply the mnemonic APGAR, for “appearance” (skin color), “pulse” (heart rate), “grimace” (reflex), “activity” (muscle tone), and “respiration.”
Of the five Apgar criteria, heart rate and respiration are the most critical. Poor scores for either of these measurements may indicate the need for immediate medical attention to resuscitate or stabilize the newborn. In general, any score lower than 7 at the 5-minute mark indicates that medical assistance may be needed. A total score below 5 indicates an emergency situation. Normally, a newborn will get an intermediate score of 1 for some of the Apgar criteria and will progress to a 2 by the 5-minute assessment. Scores of 8 or above are normal.
The first breath a newborn takes at birth inflates the lungs and dramatically alters the circulatory system, closing the three shunts that directed oxygenated blood away from the lungs and liver during fetal life. Clamping and cutting the umbilical cord collapses the three umbilical blood vessels. The proximal umbilical arteries remain a part of the circulatory system, whereas the distal umbilical arteries and the umbilical vein become fibrotic. The newborn keeps warm by breaking down brown adipose tissue in the process of nonshivering thermogenesis. The first consumption of breast milk or formula floods the newborn’s sterile gastrointestinal tract with beneficial bacteria that eventually establish themselves as the bacterial flora, which aid in digestion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?